Pediatric tibia and fibula fracture following MVA
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
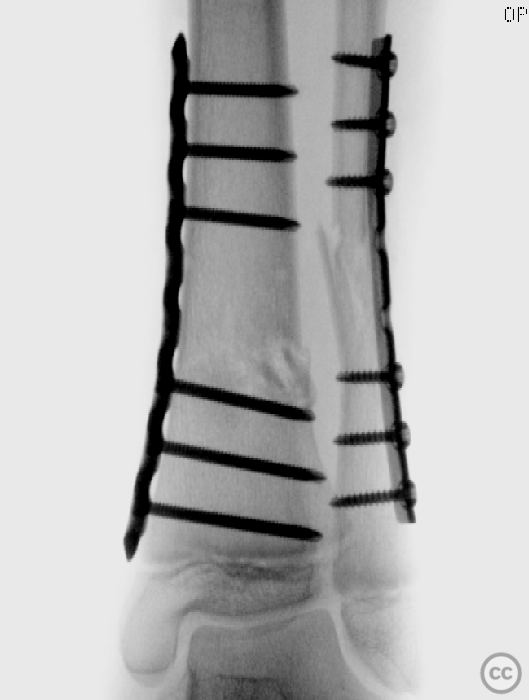
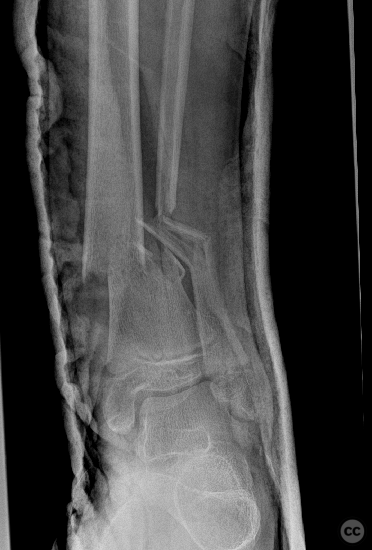
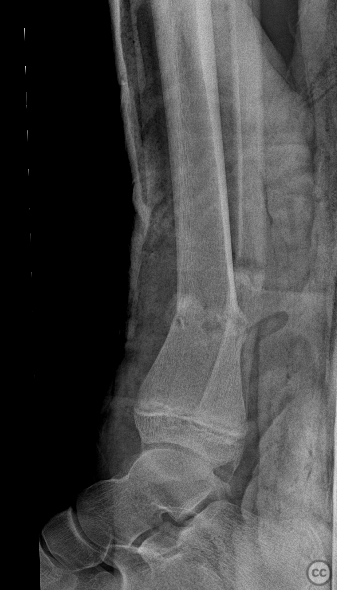
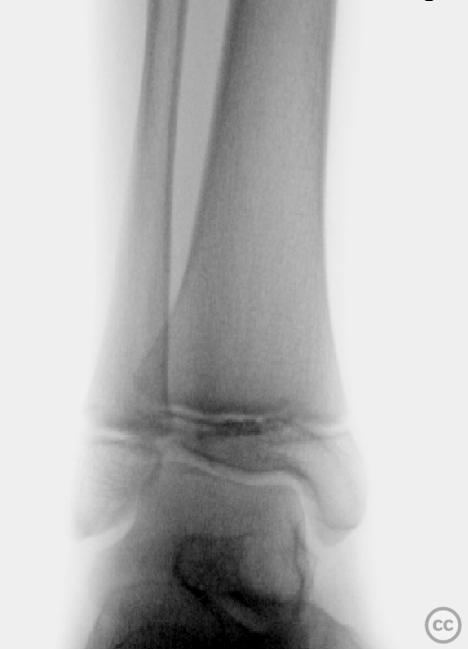
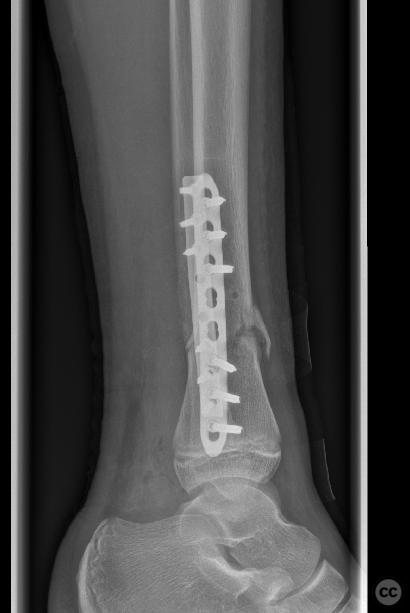
Clinical and radiological findings: A 12-year-old female involved in a high-speed motor vehicle accident, resulting in isolated lower extremity trauma. The injury was closed with an Oestern and Tscherne grade II classification. Initial radiographs revealed a transverse comminuted fracture of both the tibia and fibula with some plastic deformation. The fracture was unstable with poorly controlled reduction attempts. No indication of compartment syndrome.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: ORIF and dual plating
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine
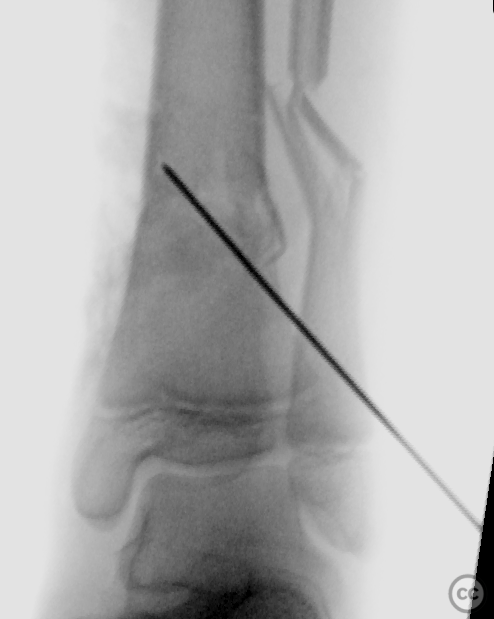
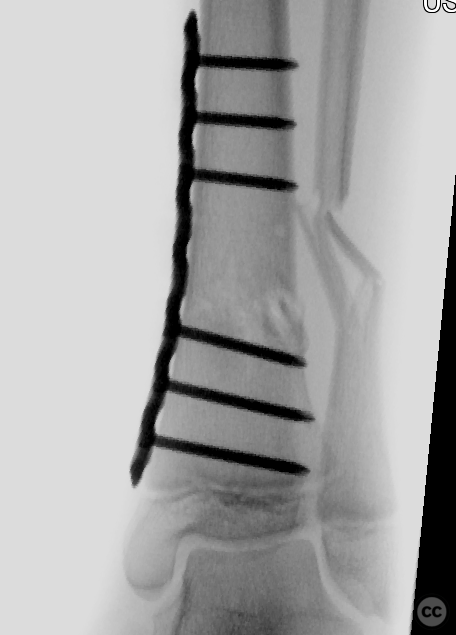
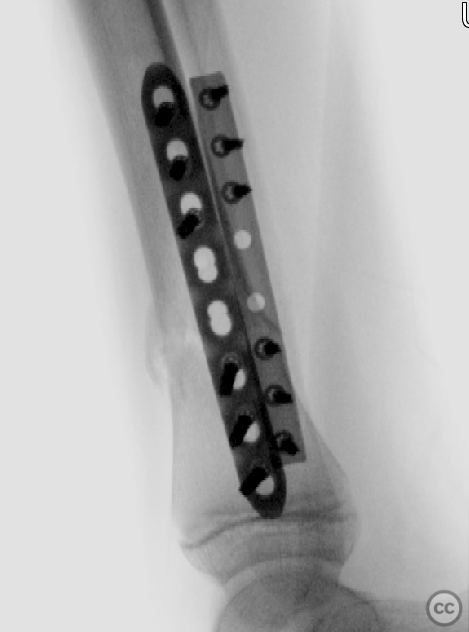
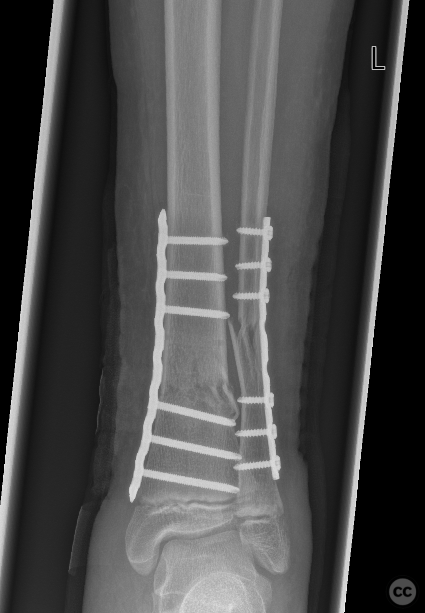
Operative remarks:The surgery commenced with a medial approach to the tibia. The deformity tended into valgus due to a lateral tibial defect. An open reduction was performed, and provisional fixation achieved with K-wires. A 3.5mm locking compression plate (LCP) was precontoured to match the profile of the tibia, ensuring anatomical alignment by comparing it intraoperatively to the contralateral side. The fracture was reduced to the plate with cortical screws, which were then exchanged for locking screws. The fibula, which did not reduce with the tibial reduction, was addressed through a lateral approach. Disimpaction and reduction of fibular fragments were achieved, followed by stabilization with a 3.5mm one-third tubular plate.
Reflecting on the operation, the dual approach allowed for effective management of both the tibial and fibular fractures. The additional lateral approach for the fibula offered secuirty in addressing the tendency to valgus deformity. Comparing the injured leg's alignment to the uninjured side intraoperatively was a necessary step to achieving a satisfactory anatomical outcome.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, no cast or splint was applied, allowing for early mobilization. The patient was advised toe weight-bearing (TWB) for 6 weeks.
Follow up: ROH in 9 months
Orthopaedic implants used: 3.5mm LCP plate for the tibia, 3.5mm one-third tubular plate for the fibula
Search for Related Literature
Dr Ed Oates
- Germany , Schleswig Holstein
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities

Article viewed 530 times
28 Feb 2024
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Oates, E.J. (2024). Pediatric tibia and fibula fracture following MVA. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 17277967 Published Online Feb 28 2024.