Subacute 2 part proximal humerus fracture
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
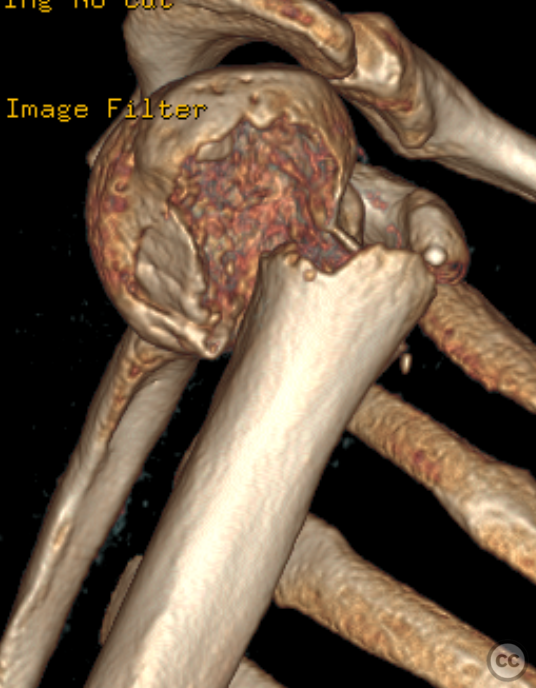
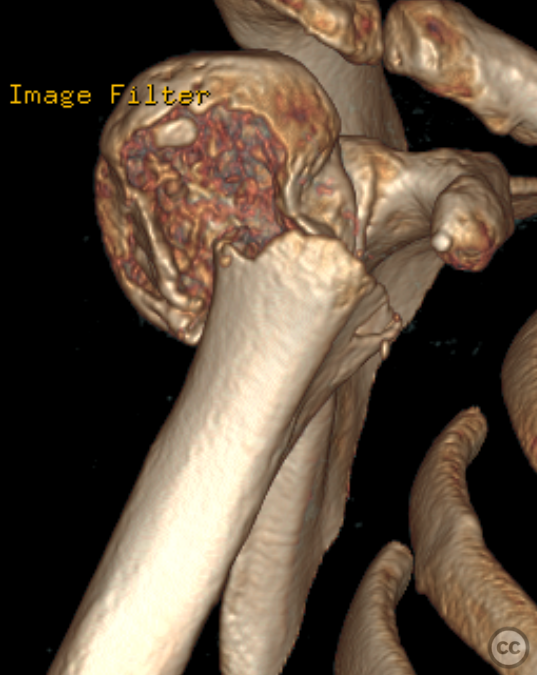
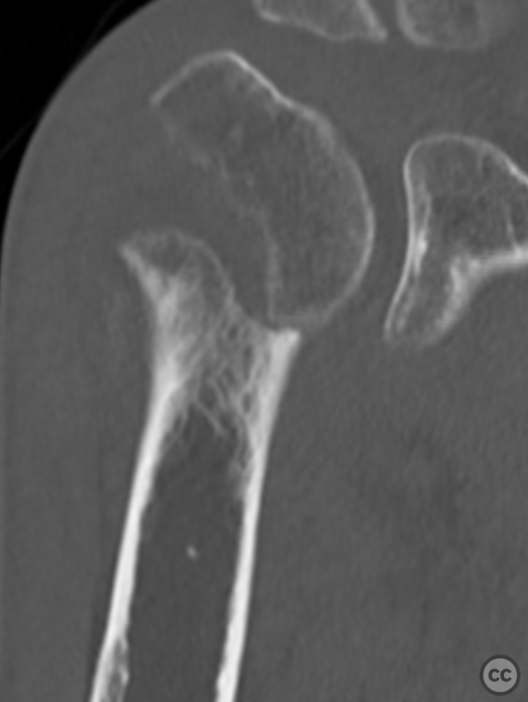
Clinical and radiological findings: A 50-year-old male with malnutrition presented with pain and limited range of motion (ROM) in the right shoulder following an unwitnessed fall at an unknown date. The patient was referred to orthopedics after a proximal humerus fracture was incidentally discovered on thoracic X-ray. The fracture is a simple two-part, grossly displaced fracture. Neurovascular examination was intact. There was a faint hematoma with green/yellow discoloration around the shoulder, indicating the injury occurred some significant time prior. The patient still experienced significant pain and restricted ROM.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: Given the subacute nature of the fracture, preoperative planning remained focused on achieving anatomical reduction and stable fixation to facilitate early mobilization. A deltopectoral approach was chosen for its direct access to the proximal humerus while preserving deltoid function. Preoperative imaging included detailed X-rays and CT scans to assess fracture pattern, displacement, and any potential bone loss.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine in a semi-beach-chair position,
Anatomical surgical approach: A deltopectoral approach was utilized
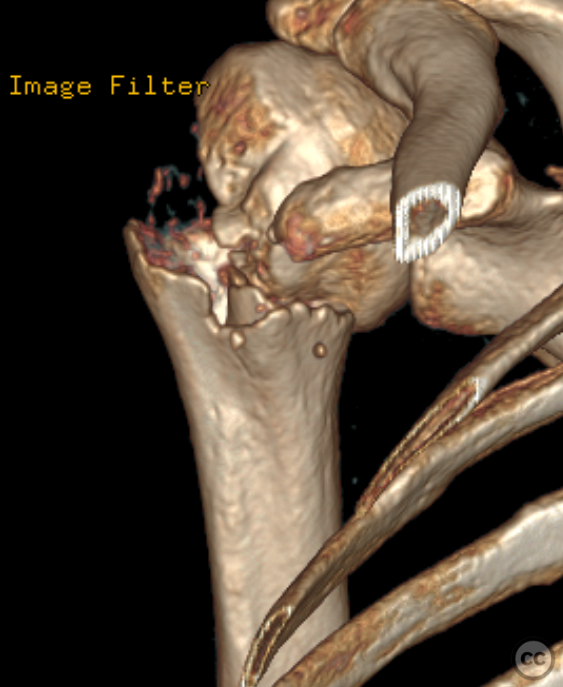
Operative remarks:Upon exploration, extensive scarring consistent with the sub acute time scale and callus formation around the deltoid muscle were noted, complicating exposure. Additionally, the long head of biceps tendon was found torn with its distal portion unidentifiable. The fracture site exhibited significant callus formation obscuring anatomical landmarks; meticulous debridement was performed to mobilize fragments for reduction. Anatomical reduction was achieved under direct vision and provisionally held with Kirschner wires. Challenges encountered included managing soft tissue adhesions without compromising vascular supply or further damaging muscle integrity. A PHILOS plate was positioned optimally as confirmed by multiplanar fluoroscopy before final screw fixation ensuring angular stability.
Postoperative protocol: Immediate postoperative protocol encouraged full range of motion exercises within pain tolerance limits. Non-weight bearing instructions were given for 6 weeks post-operatively followed by weight-bearing as tolerated, gradually increasing activity levels based on clinical assessment and radiographic evidence of union.
Orthopaedic implants used: PHILOS (Proximal Humerus Internal LOcking System) Plate - Kirschner wires for provisional fixation
Search for Related Literature
Dr Ed Oates
- Germany , Schleswig Holstein
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities












Article viewed 766 times
05 Feb 2024
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Oates, E.J. (2024). Subacute 2 part proximal humerus fracture. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 17571183 Published Online Feb 05 2024.