Displaced Surgical Neck Fracture with minimally invasive approach
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
Clinical and radiological findings: A 65-year-old female sustained a fall from standing height, resulting in a displaced surgical neck fracture of the humerus with medial displacement of the diaphysis and a non-displaced fracture of the greater tuberosity. Initial radiographs confirmed the fracture pattern, and neurovascular examination was unremarkable.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The planned surgical approach involved a minimally invasive technique to reduce the surgical neck fracture and stabilize it using a proximal humeral locking plate. The greater tuberosity fracture, being non-displaced, did not require direct intervention.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned in a beach chair position with a C-arm fluoroscope for intraoperative imaging.
Anatomical surgical approach: A minimally invasive anterolateral approach was utilized. A small incision was made over the deltoid muscle, and subdeltoid dissection was performed to expose the proximal humerus. The fracture site was visualized, and reduction was achieved using percutaneous techniques.
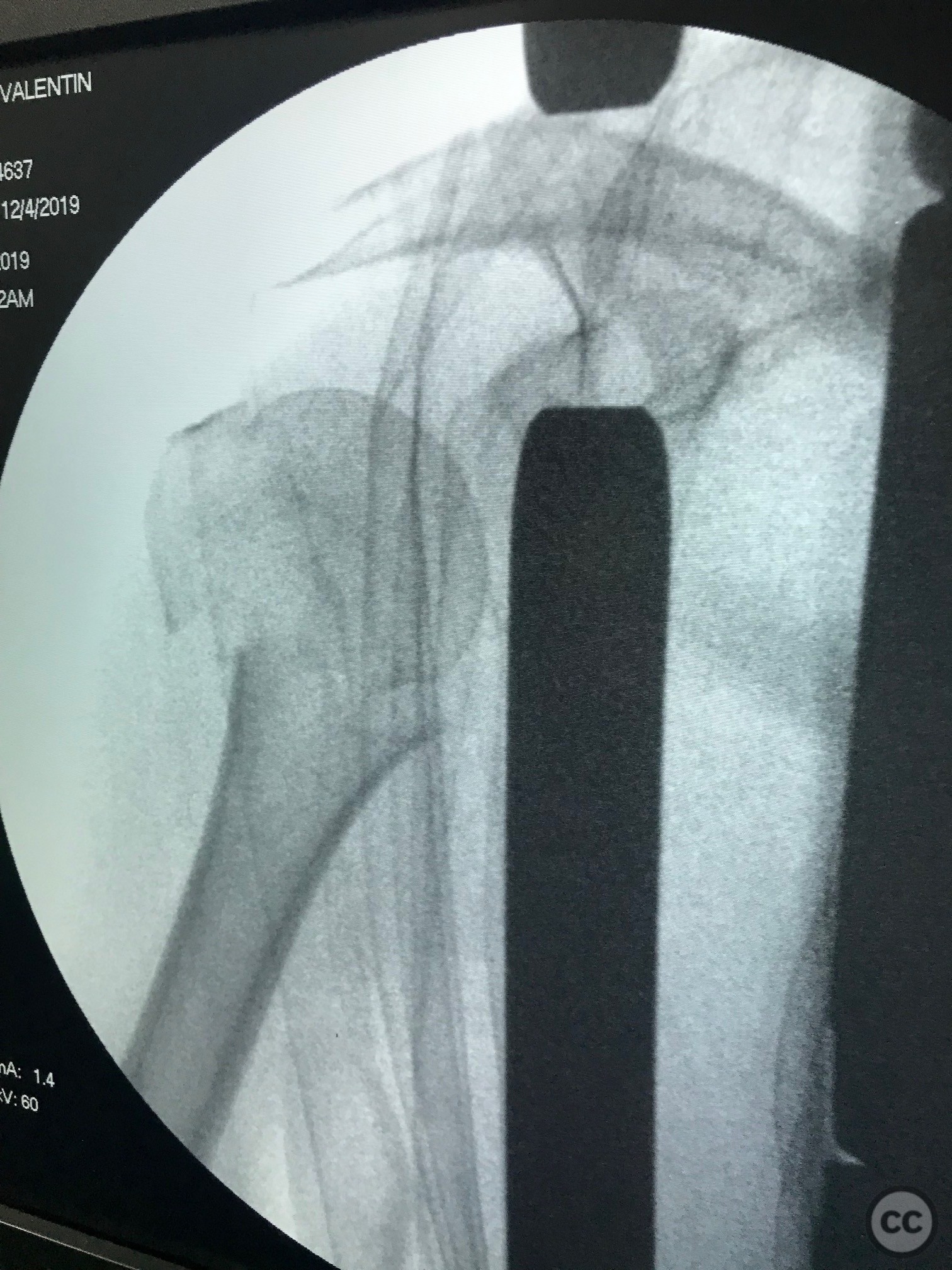
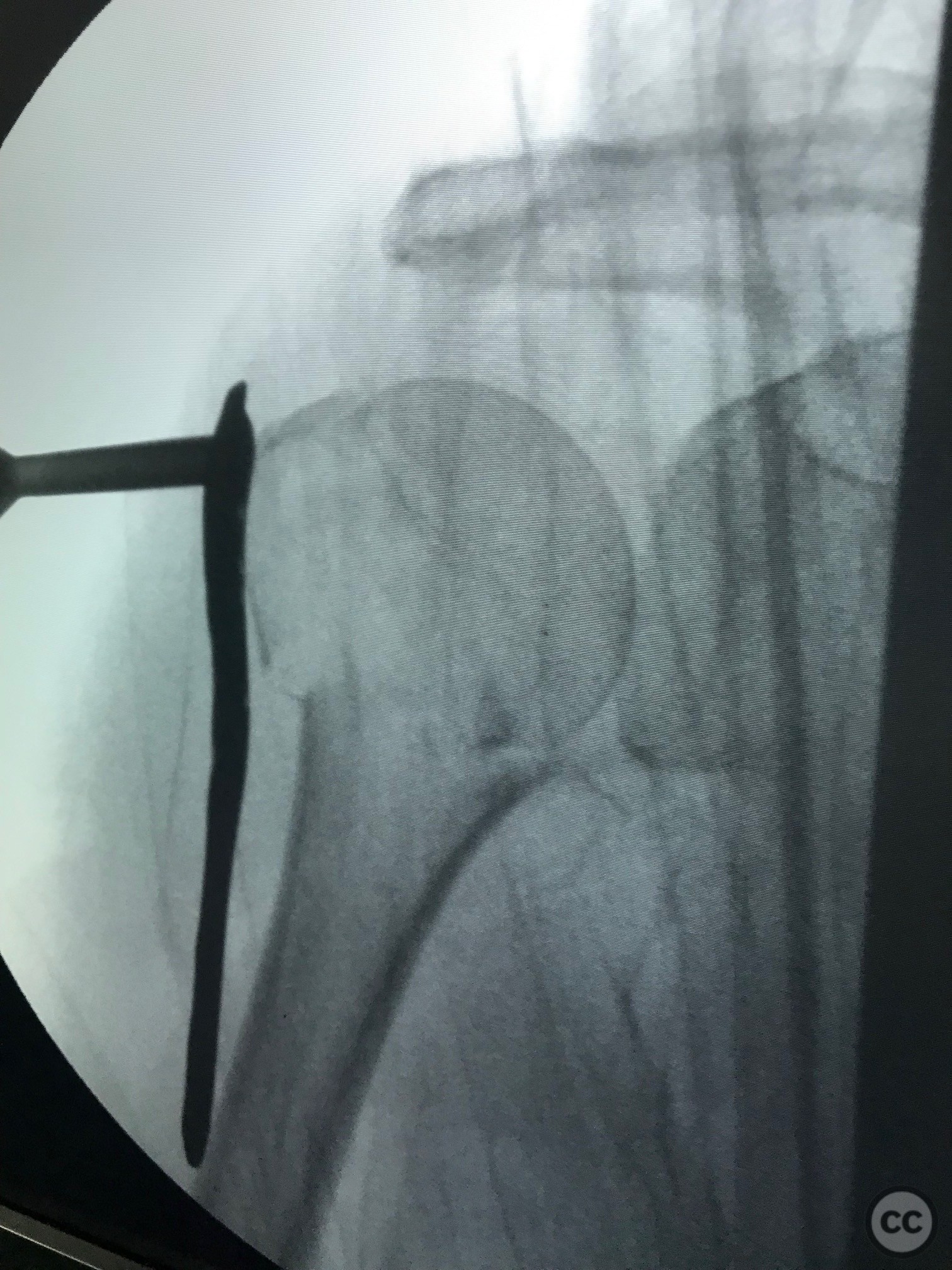
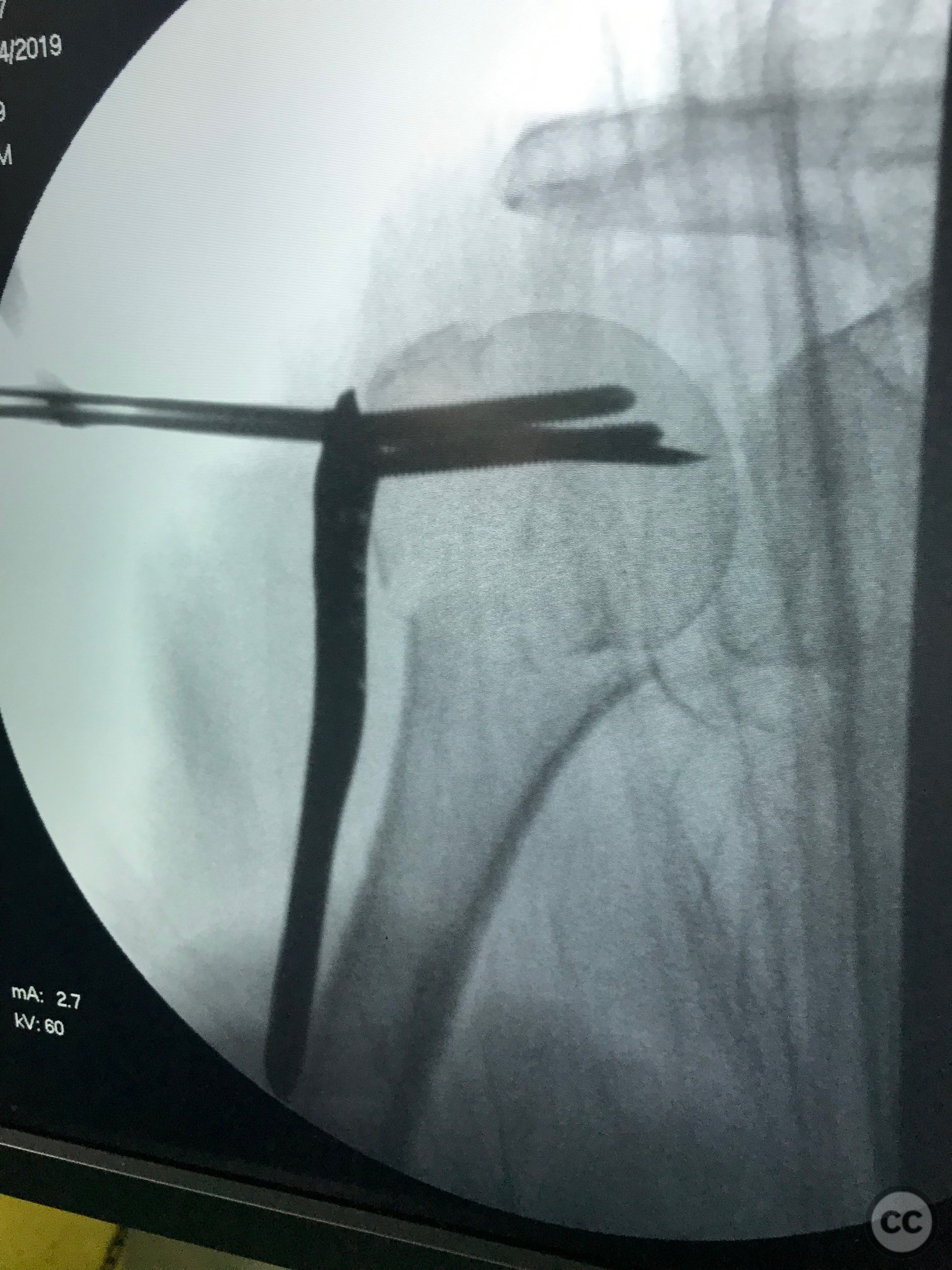
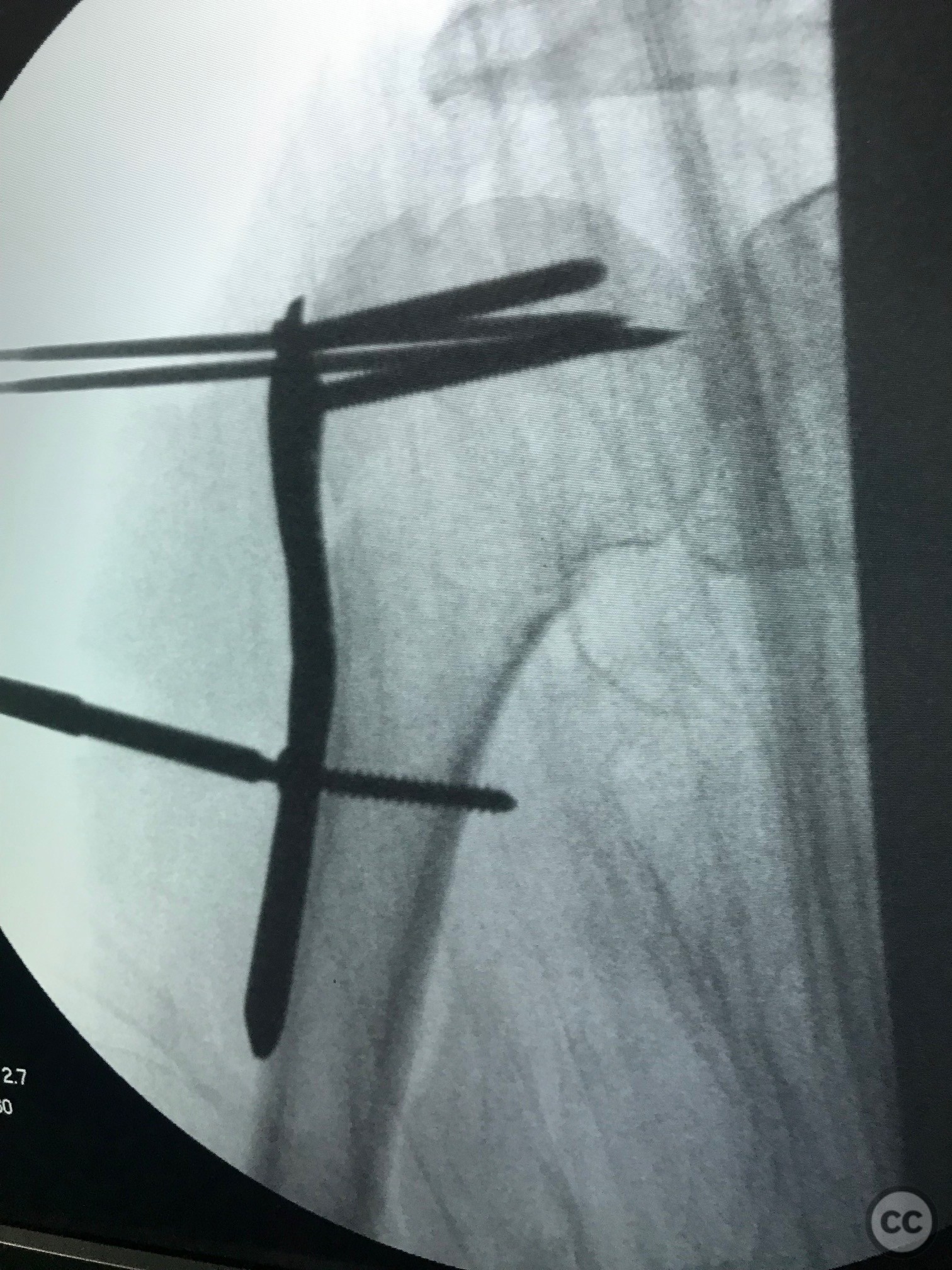
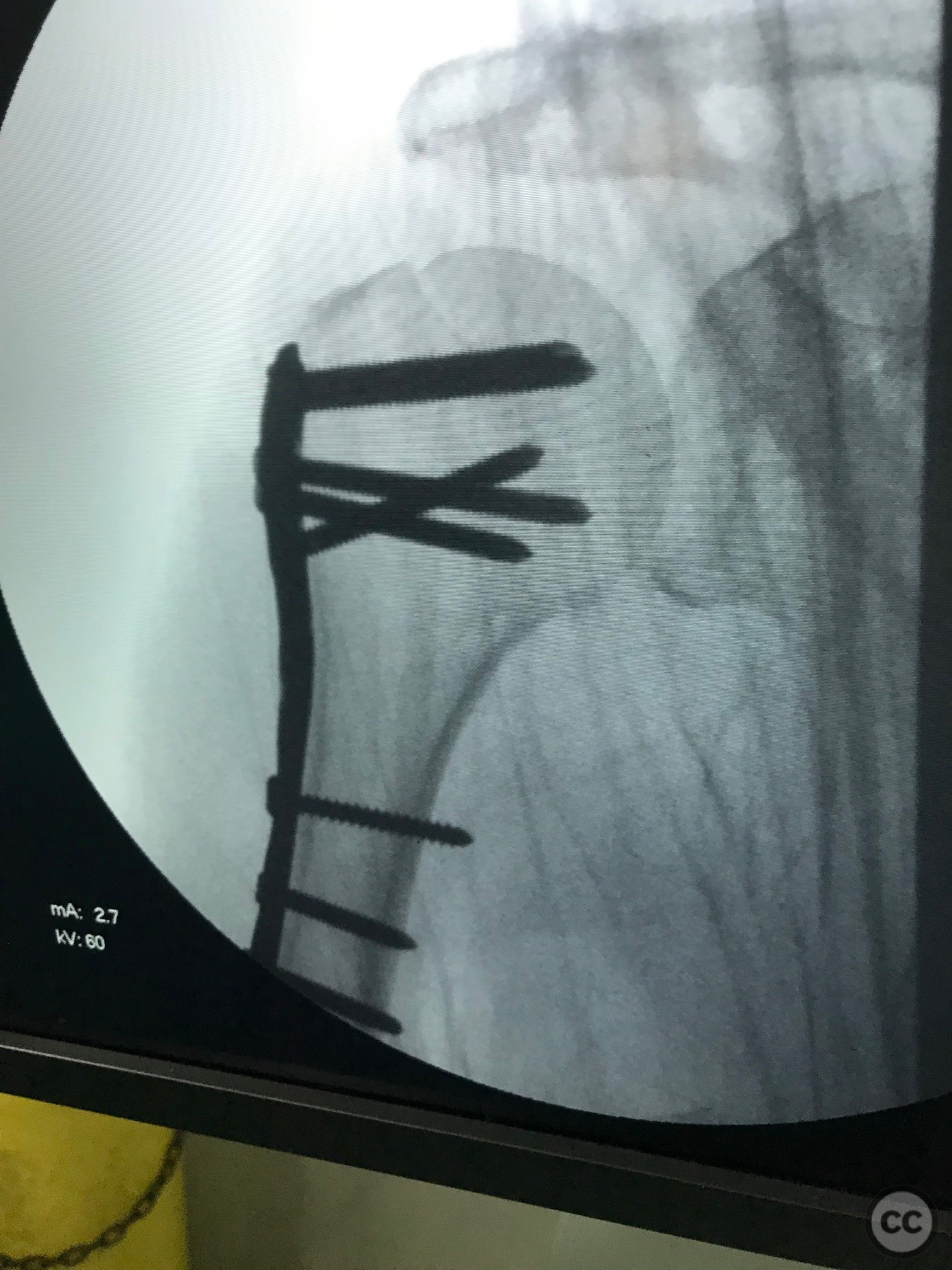
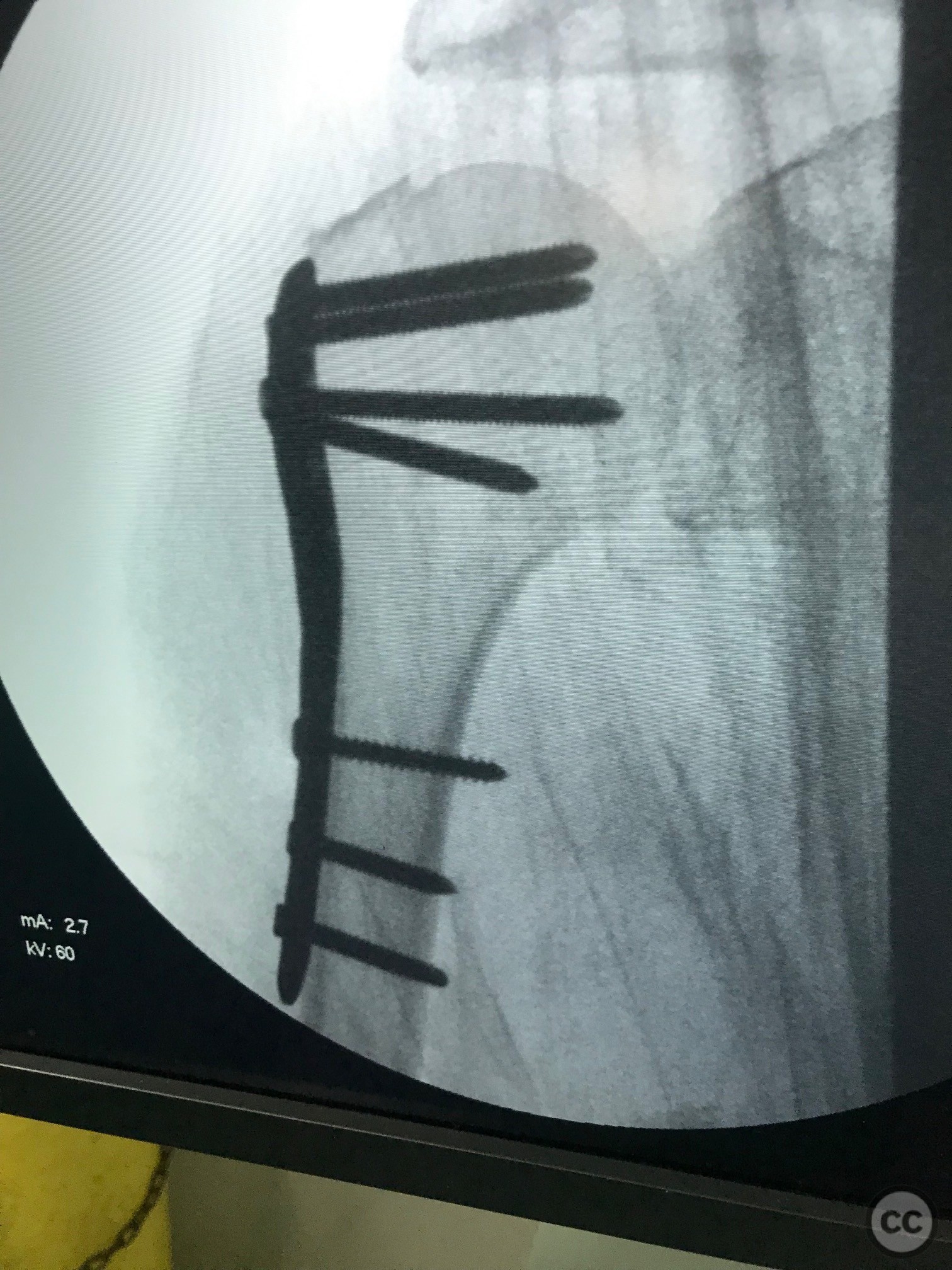
Operative remarks:Proximal screws were inserted into the head of the humerus (Fila A) and secured with Kirschner wires to maintain temporary stability. Once the plate and proximal screws were confirmed to be in adequate position via fluoroscopy, the medial displacement of the diaphysis was reduced using a cortical screw. Final fixation was completed by inserting diaphyseal screws.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperatively, the patient was advised to wear a shoulder immobilizer during the day for 4 weeks. Passive range of motion exercises were initiated immediately, progressing to active-assisted exercises at 6 weeks post-surgery. Full weight-bearing and unrestricted activities were allowed by 12 weeks postoperatively.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: Proximal humeral locking plate, Kirschner wires, cortical screw
Search for Related Literature
Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities


Article viewed 524 times
18 Jul 2024
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
LUIS LEONCIO TEMOCHE DIAZ. (2024). Displaced Surgical Neck Fracture with minimally invasive approach. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 22203787 Published Online Jul 18 2024.