Osteosynthesis of Segmental Humerus Fracture with Extended Deltopectoral Approach
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
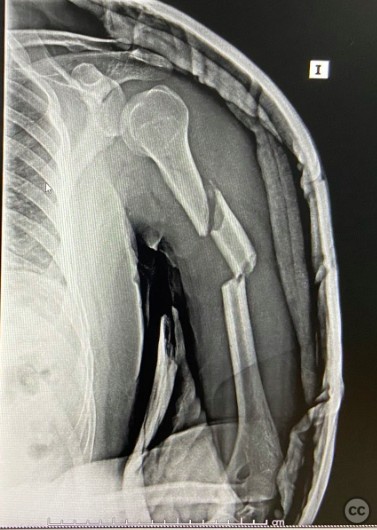
Clinical and radiological findings: A 38-year-old male involved in a high-speed vehicular accident presented with a segmental fracture of the left humerus. The injury was isolated with no additional reported systemic or local complications.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan included osteosynthesis utilizing a long proximal humerus plate. An extended deltopectoral approach was chosen for adequate exposure of the fracture site, allowing for direct visualization and manipulation of the fracture fragments. The radial nerve was to be explored and protected throughout the procedure, especially at the distal aspect of the surgical field.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine with the left arm abducted and externally rotated on an arm table, ensuring full access to the anterolateral aspect of the shoulder and upper arm.
Anatomical surgical approach: The surgical approach commenced with an extended deltopectoral incision. Following the incision, careful dissection was performed to protect the cephalic vein and deltopectoral interval was identified and utilized for deeper access. The deltoid muscle was retracted laterally, and the pectoralis major medially, exposing the humerus. Subperiosteal dissection allowed visualization of the fracture site. The radial nerve was identified at its distal passage, isolated, and protected throughout the procedure.
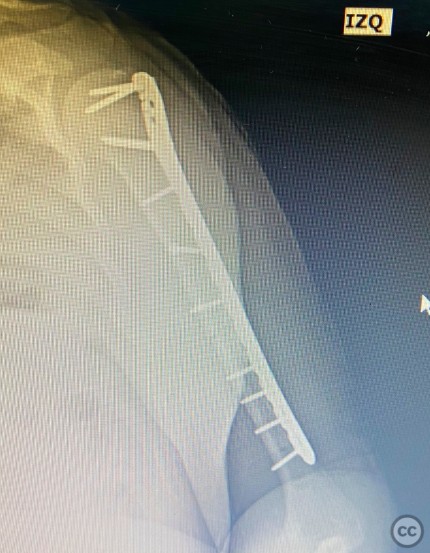
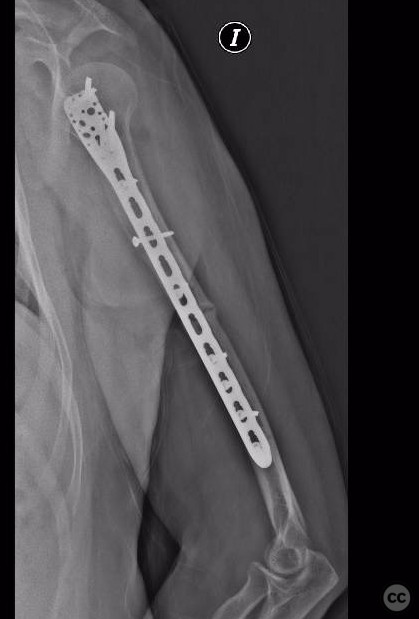
Operative remarks:Intraoperatively, the segmental fracture was addressed by first reducing the proximal fragment using reduction forceps. An interfragmentary screw was placed in the proximal portion of the fracture to stabilize the initial reduction. Subsequently, a long proximal humerus plate was applied in compression mode to address and stabilize the distal portion of the fracture. Careful attention was paid to avoid radial nerve injury during hardware placement.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation protocol included immediate passive range of motion exercises within pain limits. Active range of motion and strengthening exercises were gradually introduced based on fracture healing and patient tolerance.
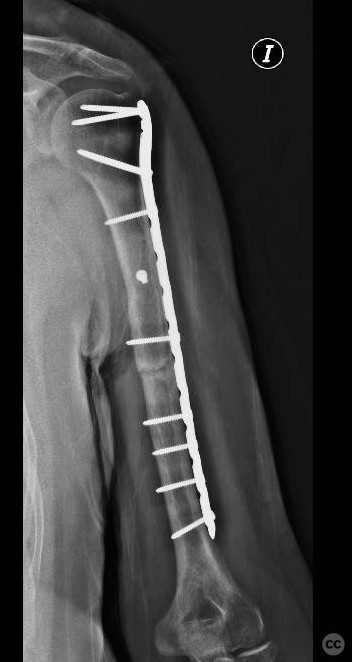
Follow up: Six months postoperatively, the patient presented with nonunion of the distal fracture segment. Surgical intervention was recommended; however, the patient was lost to follow-up with no further records available.
Orthopaedic implants used: Orthopaedic implants used: Long proximal humerus plate, interfragmentary screw.
Search for Related Literature
Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities




Article viewed 549 times
17 Mar 2024
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
LUIS LEONCIO TEMOCHE DIAZ. (2024). Osteosynthesis of Segmental Humerus Fracture with Extended Deltopectoral Approach. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 25604464 Published Online Mar 17 2024.