Proximal Humerus Fracture with Medialization: Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
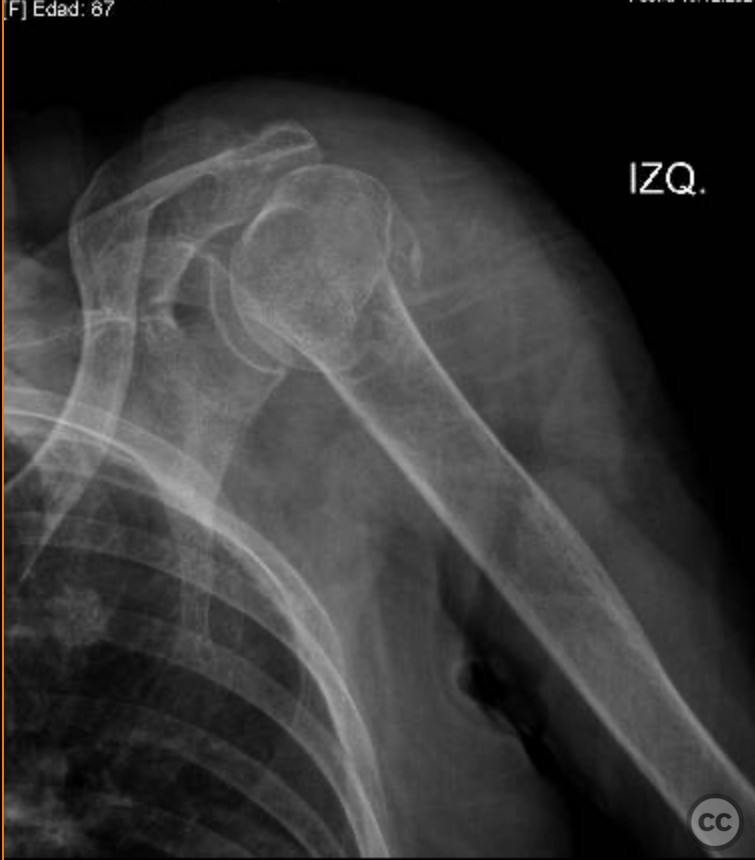
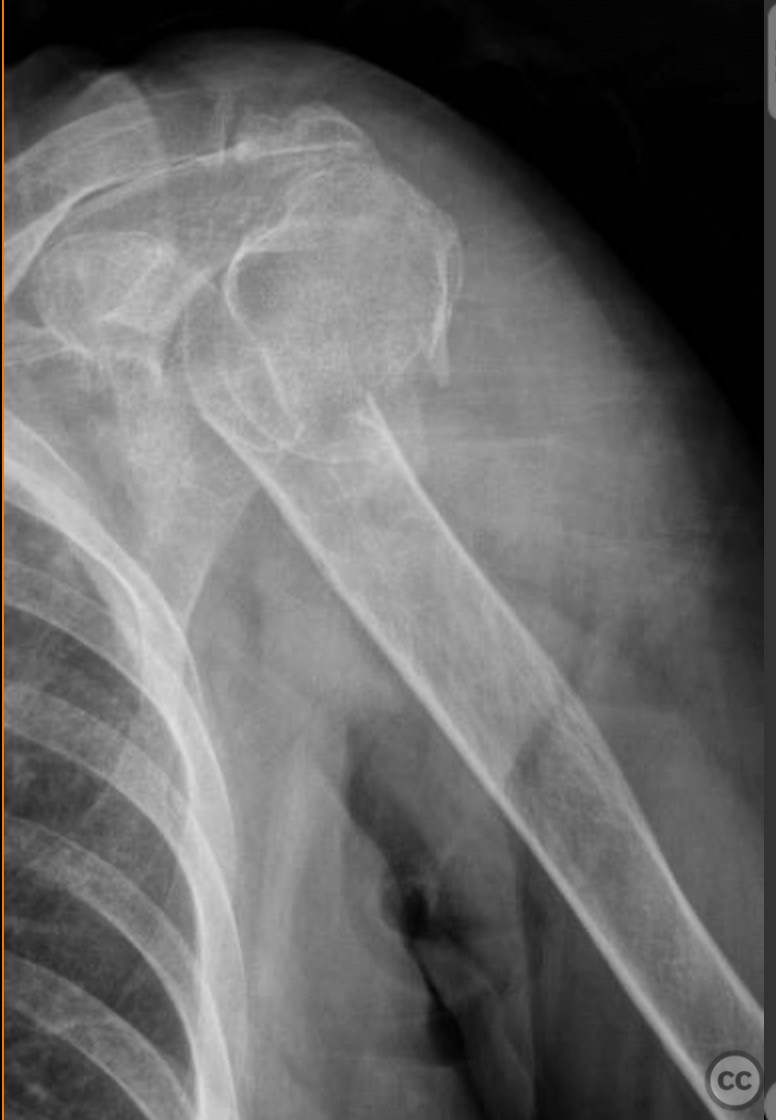
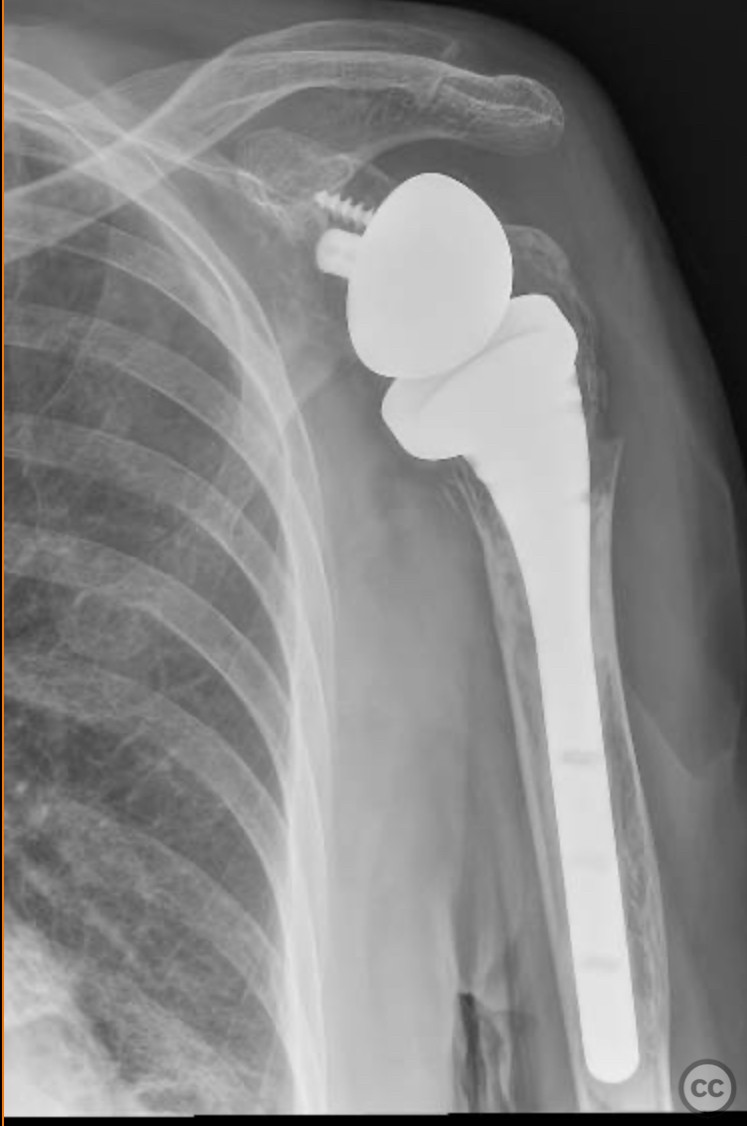
Clinical and radiological findings: An 83-year-old active female with no significant comorbidities sustained a proximal humerus fracture. Initially managed conservatively, follow-up at two weeks post-injury revealed fracture displacement with complete medialization of the diaphysis. The patient continued to experience significant pain, prompting surgical intervention with reverse shoulder arthroplasty.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved a deltopectoral approach to access the proximal humerus. The surgical team planned for a humeral head osteotomy, placement of a glenosphere, and a cemented humeral stem. Osteosynthesis of the tuberosities was to be performed using transosseous sutures and humeral head grafting.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned in a beach chair position to facilitate the deltopectoral approach and optimize surgical access to the shoulder joint.
Anatomical surgical approach: A deltopectoral approach was utilized, involving an incision along the deltopectoral groove. The cephalic vein was preserved, and the deltoid muscle was retracted laterally. Subperiosteal dissection was performed to expose the proximal humerus.
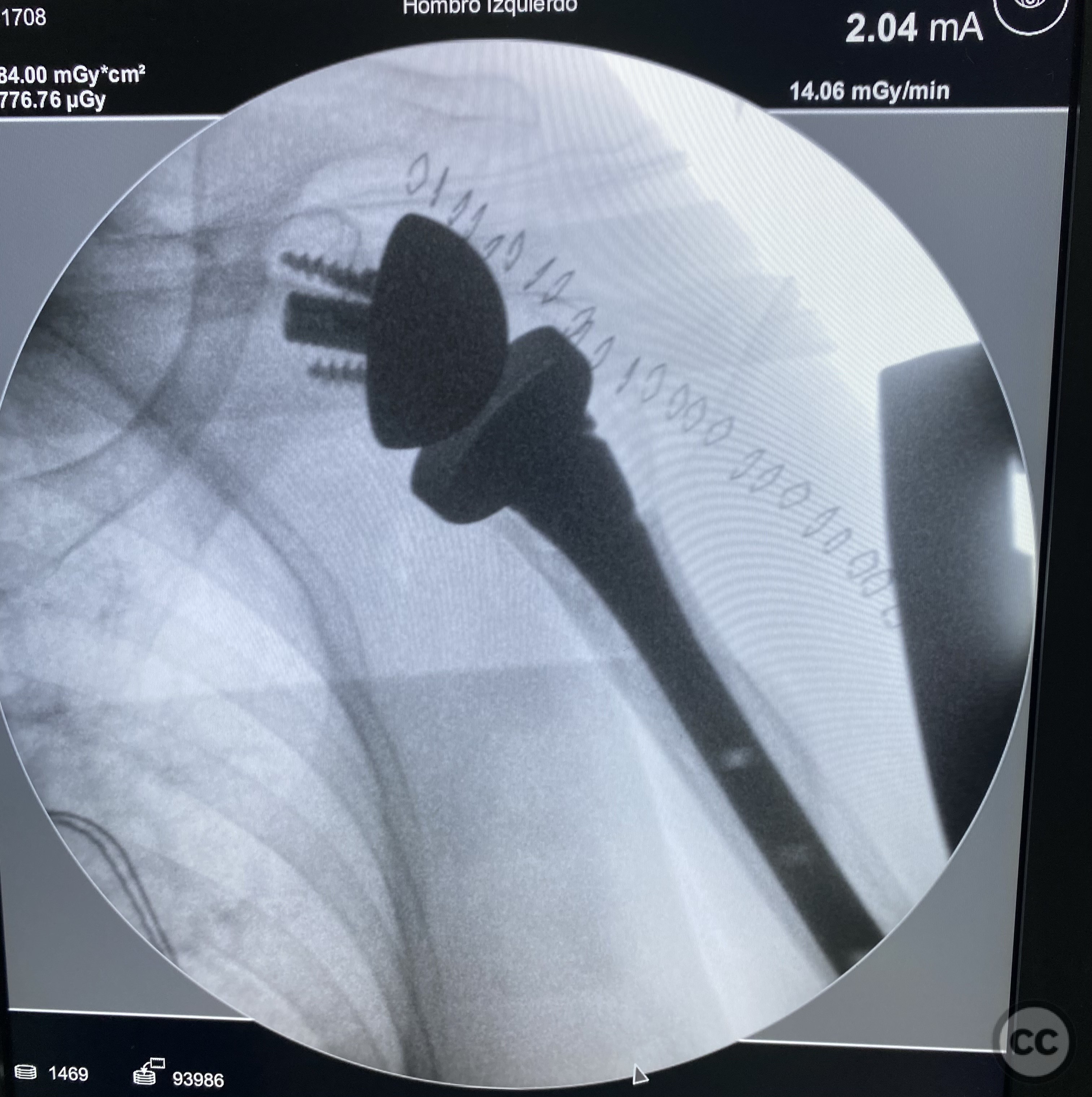
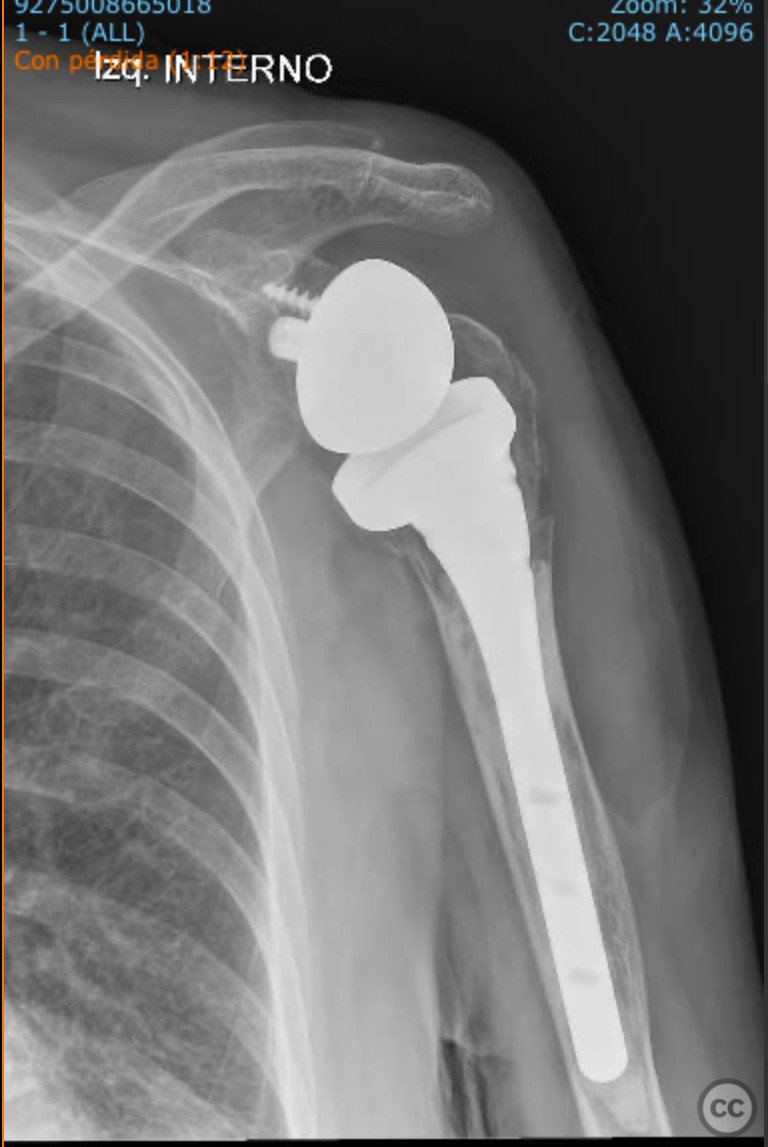
Operative remarks:Intraoperatively, a humeral head osteotomy was performed to remove the fractured head. A glenosphere was placed on the glenoid, and a cemented humeral stem was inserted into the humeral canal. Osteosynthesis of the tuberosities was achieved using transosseous sutures combined with a graft from the excised humeral head.
Postoperative protocol: The surgical team noted that the medialization of the diaphysis required careful handling during the procedure to ensure proper alignment and fixation of the tuberosities. The use of transosseous sutures provided stable fixation, and the humeral head graft facilitated healing.
Follow up: Postoperatively, the patient followed a rehabilitation protocol involving immobilization in a sling for four weeks, with passive range of motion exercises initiated after two weeks. Active-assisted exercises were introduced at six weeks, progressing to active range of motion and strengthening exercises by three months post-surgery.
Orthopaedic implants used: Not specified.
Search for Related Literature
Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities


Article viewed 167 times
12 Jan 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
LUIS LEONCIO TEMOCHE DIAZ. (2025). Proximal Humerus Fracture with Medialization: Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 29758981 Published Online Jan 12 2025.