Tibial Plateau Fracture: Posterolateral Depression with Posterior Cortical Crack
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
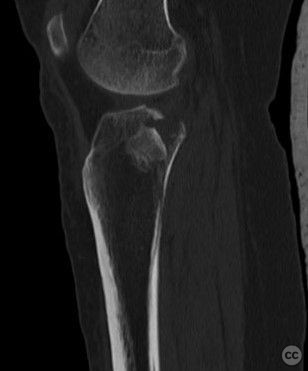
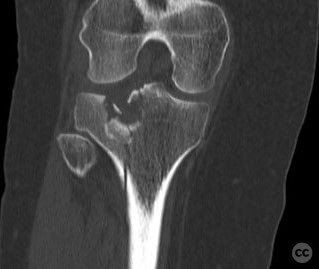
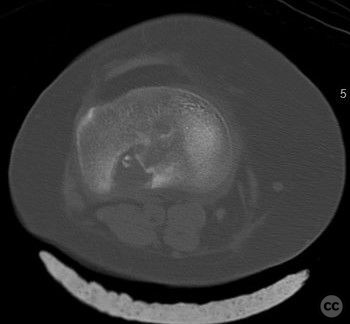
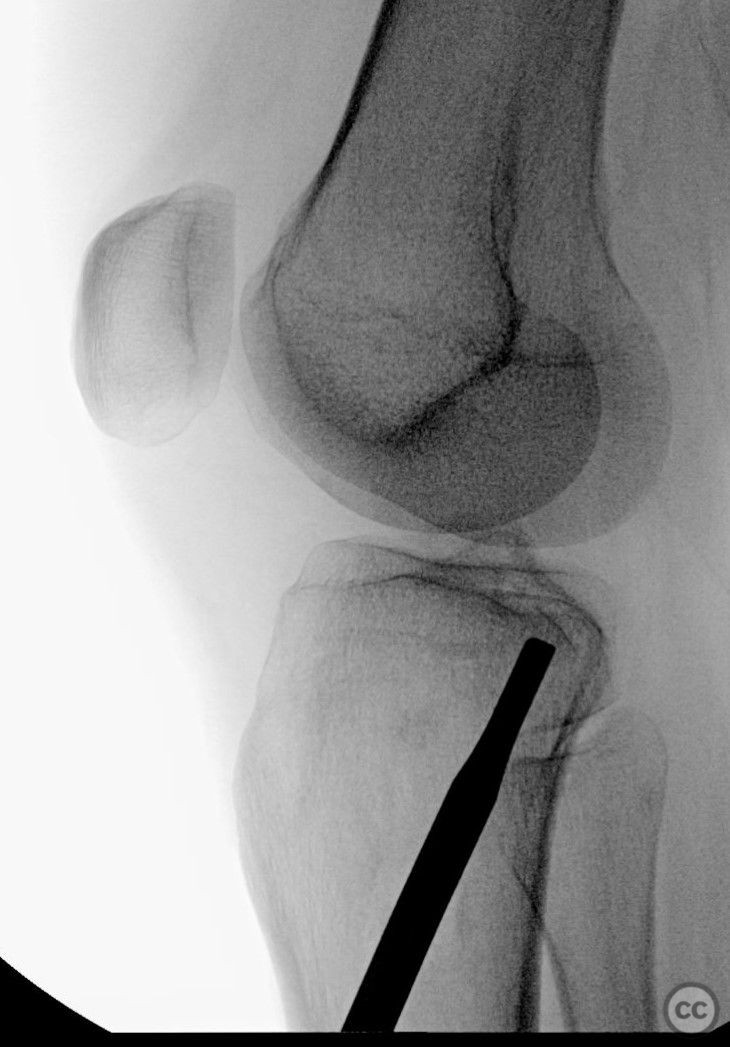
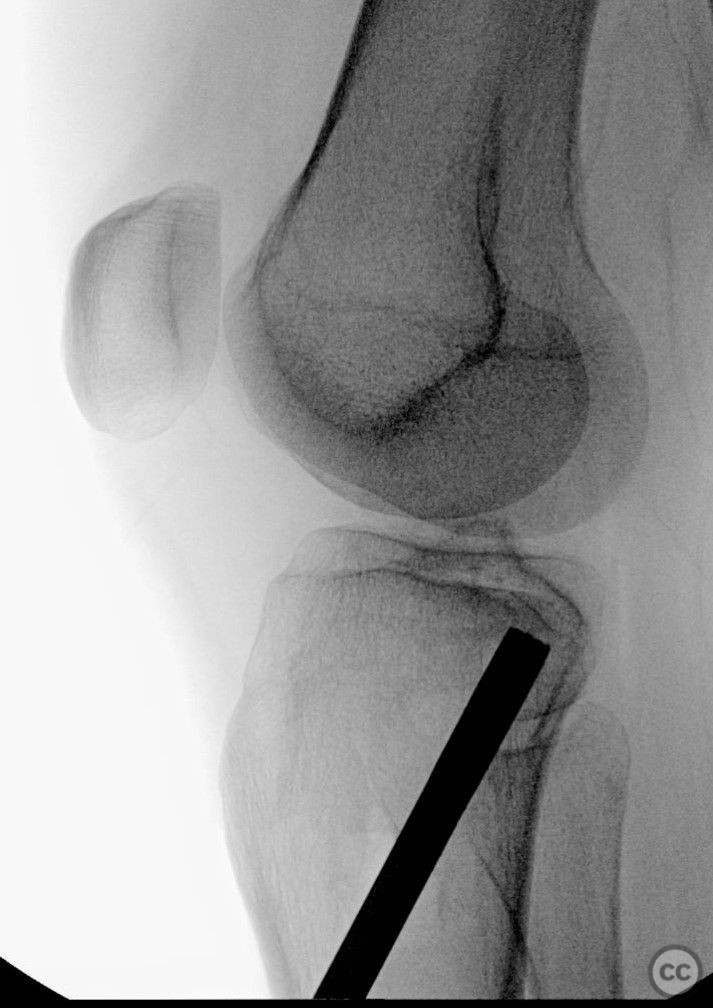
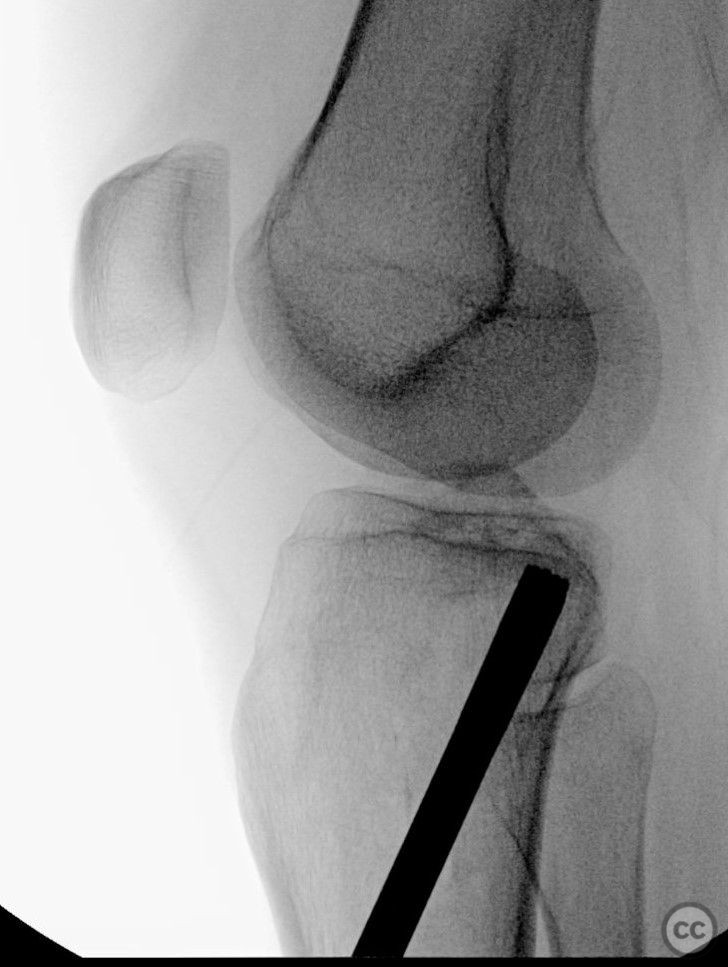
Clinical and radiological findings: A 34-year-old female involved in a buggy accident presented with a tibial plateau fracture characterized by a pure depression and a longitudinal posterior cortical crack without any split component. The patient initially refused surgical intervention. Following the injury, an intramuscular injection led to a gluteal abscess, necessitating two sessions of incision, drainage, and debridement, after which the C-reactive protein level decreased to 6.
Preoperative Plan
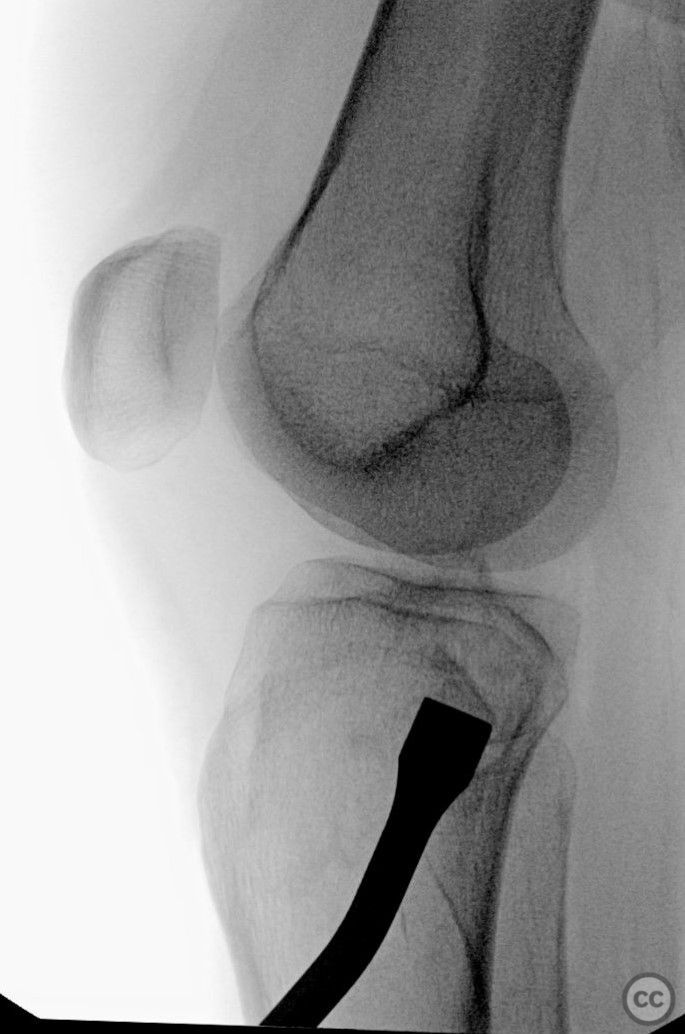
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan included closed reduction through a lateral cortical window and fixation using 3.5 mm screws. An injectable bone graft was also planned to address the depression and enhance the structural integrity of the tibial plateau. Consideration was given to the addition of an anteroposterior screw for increased rigidity, although the biomechanical stability was deemed sufficient with the injectable bone substitute.
Surgical Discussion
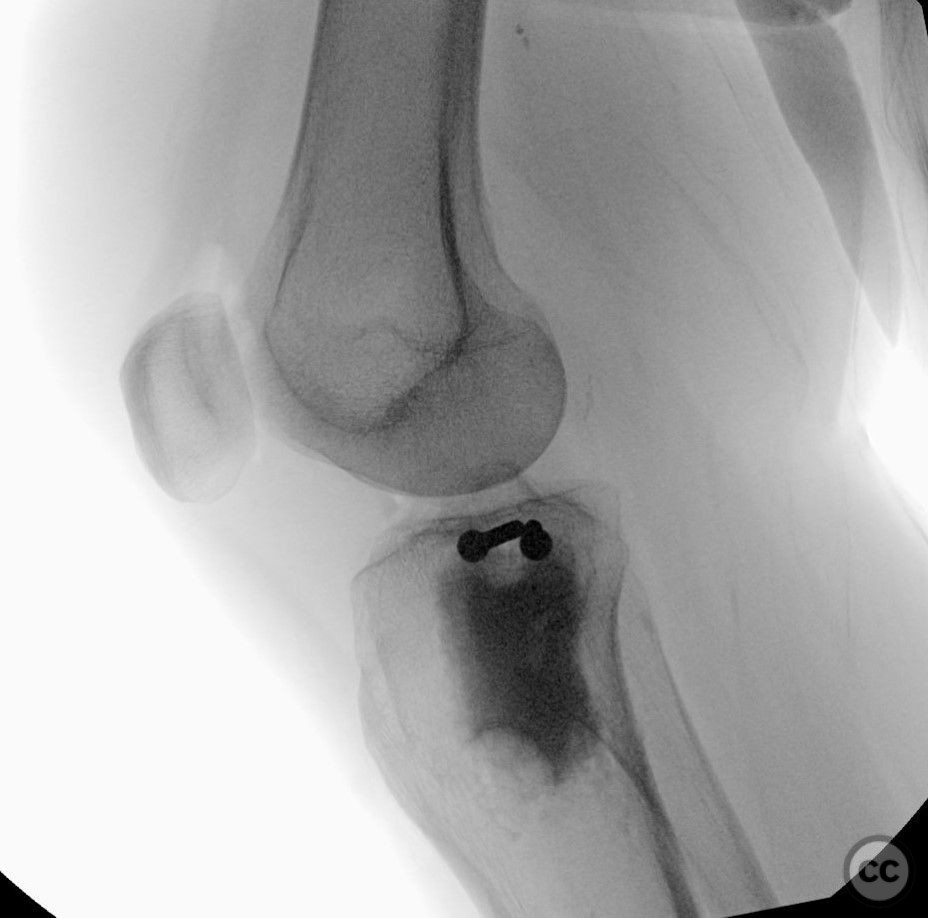
Operative remarks:Intraoperatively, attention was paid to achieving an anatomically accurate reduction of the depressed articular surface through the lateral window. The longitudinal posterior cortical crack was identified as a result of hoop stress failure. Fixation was achieved using 3.5 mm screws placed perpendicular to the fracture plane, ensuring no shear forces were applied to the fracture pattern. Injectable bone graft was used to fill the defect and support the reconstructed plateau.
Postoperative protocol: Not specified.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: 3.5 mm screws, Injectable bone graft. Originally posted on LinkedIn by Metwally Sayed Ahmad Metwally
Author's Resources & References
Search for Related Literature
Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities



Article viewed 417 times
19 Mar 2024
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
LinkedIn. (2024). Tibial Plateau Fracture: Posterolateral Depression with Posterior Cortical Crack. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 41582265 Published Online Mar 19 2024.