Tibial and fibula fracture with Metatarsal Fracture-dislocation
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
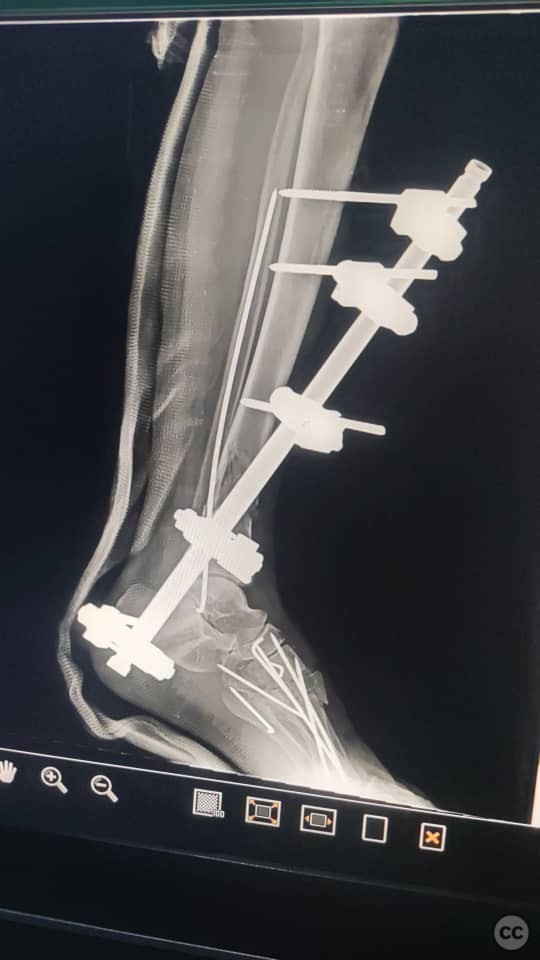
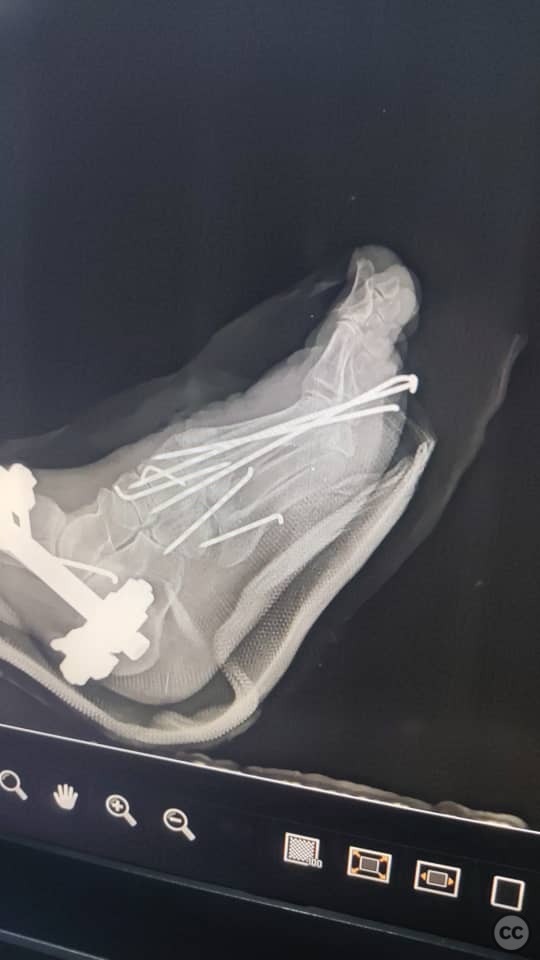
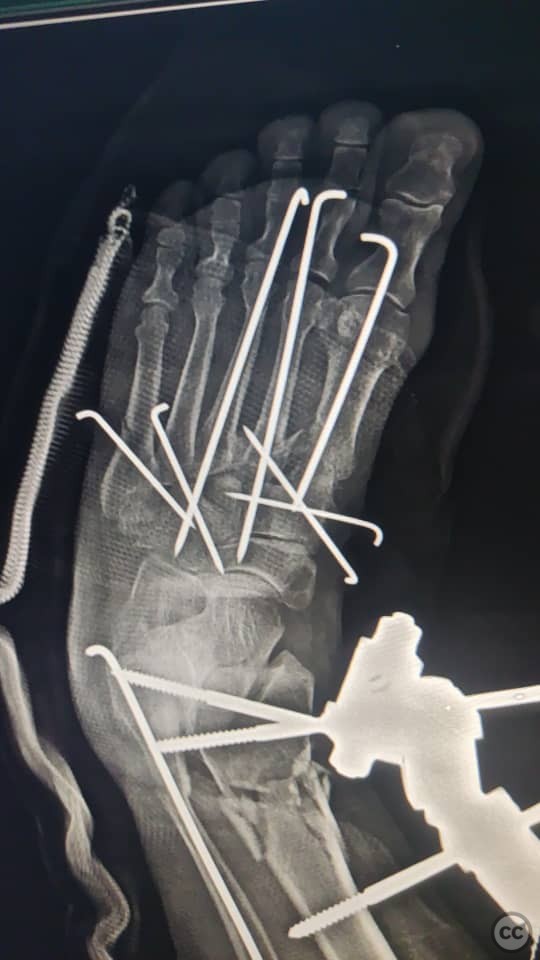
Clinical and radiological findings: A 67-year-old female presented with a tibial fracture and fracture-dislocation of the metatarsals. The patient had a history of uncontrolled hypertension and diabetes mellitus, with an initial blood glucose level of 430 mg/dL and an HbA1c of 10%. On the operating table, the patient's SpO2 was 61%, prompting a CT scan to rule out pulmonary embolism.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved stabilization of the tibial fracture using an external fixator and intramedullary K-wire fixation of the fibula. Additionally, dorsal incisions on the foot were planned for reduction and fixation of the metatarsal fractures using retrograde K-wires.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: Supine position on the operating table.
Anatomical surgical approach: The surgical approach included the application of an external fixator spanning the ankle joint for tibial stabilization. An intramedullary K-wire was inserted into the fibula. Two dorsal incisions were made on the foot to allow for reduction of the fracture-dislocation and retrograde K-wire fixation of the metatarsals. A plaster cast was applied to the foot postoperatively.
Operative remarks:Due to the patient's compromised general condition, rapid external fixation was necessitated. The external fixator provided immediate stabilization, while the K-wires allowed for alignment and stabilization of the fibula and metatarsals. The patient's critical condition required prompt intervention to prevent further complications.
Postoperative protocol: Partial weight-bearing was initiated at week 6 postoperatively.
Follow up: Not specified.
Orthopaedic implants used: External fixator, Kirschner wires (K-wires).
Search for Related Literature
Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities



Article viewed 596 times
12 Feb 2025
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
ibraheem. (2025). Tibial and fibula fracture with Metatarsal Fracture-dislocation. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 43583674 Published Online Feb 12 2025.