Mason and Molly Type 3 Posterior Malleolus Fracture with Transsyndesmotic Fibula Fracture
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
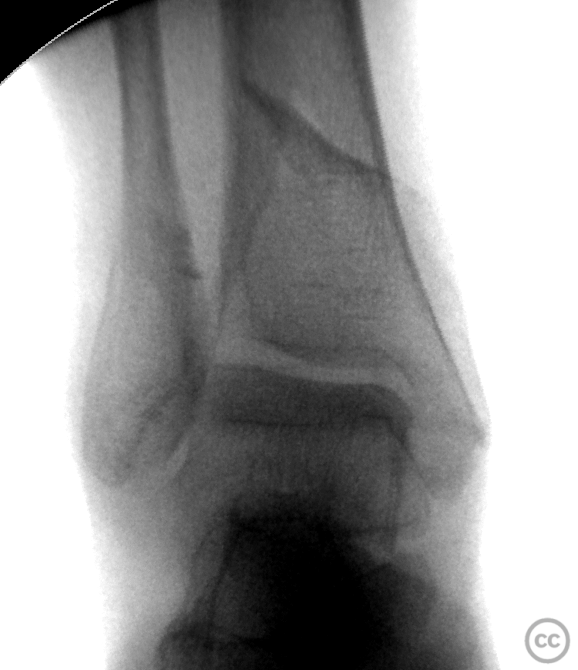
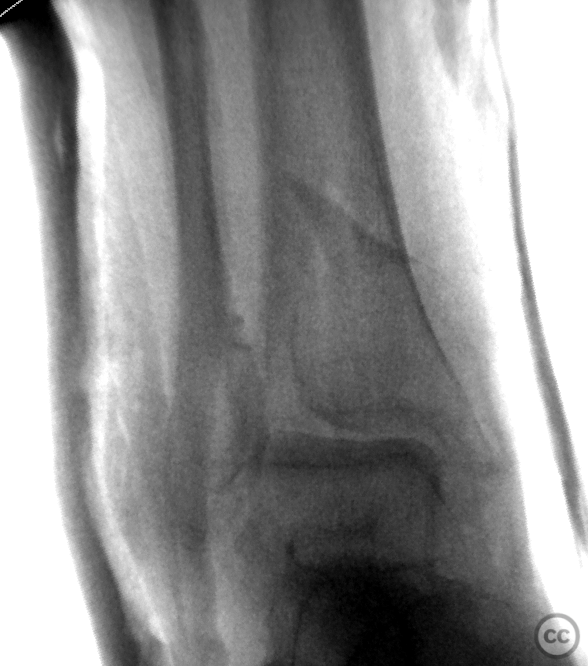
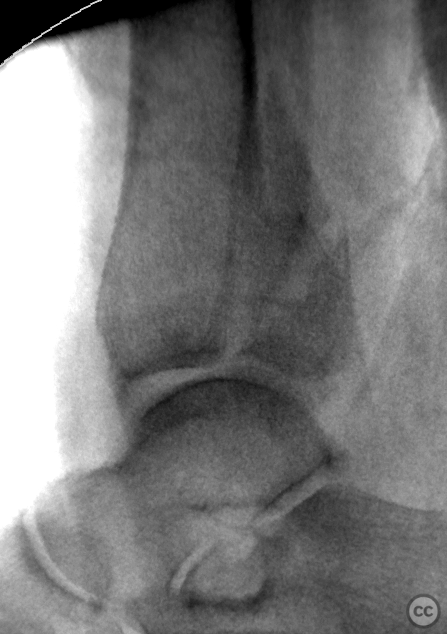
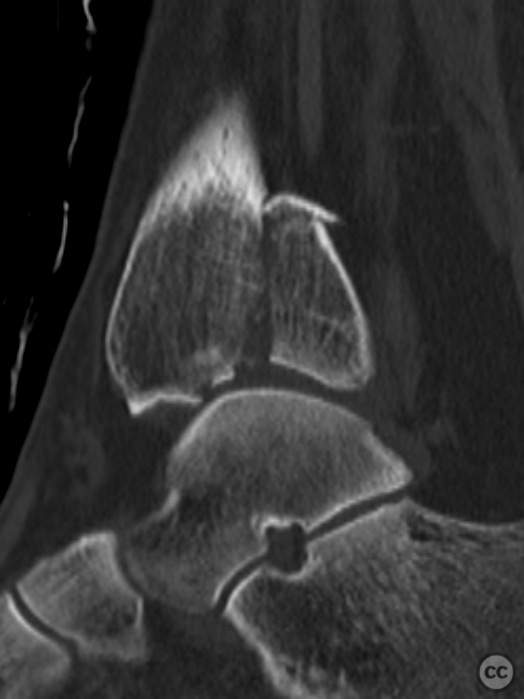
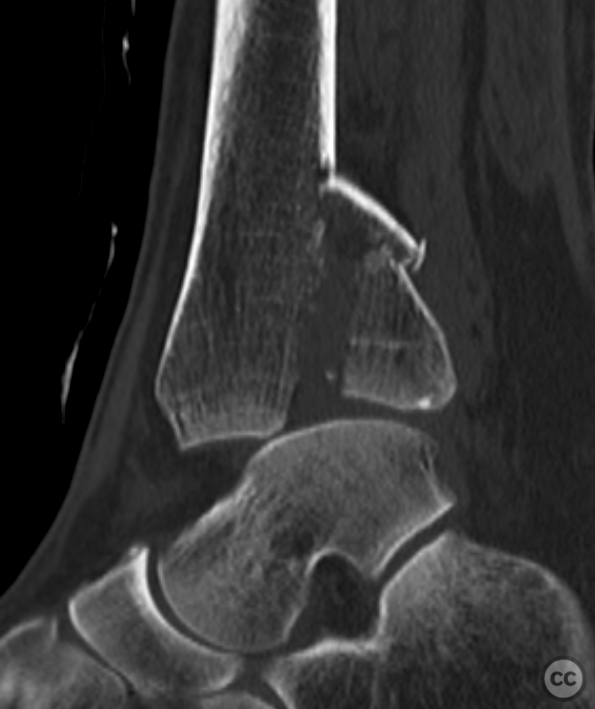
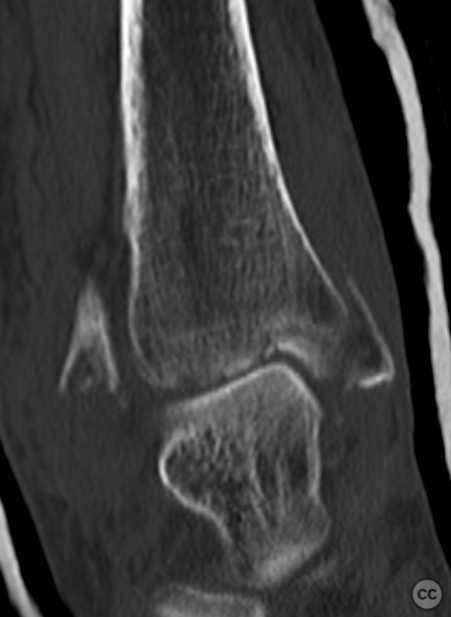
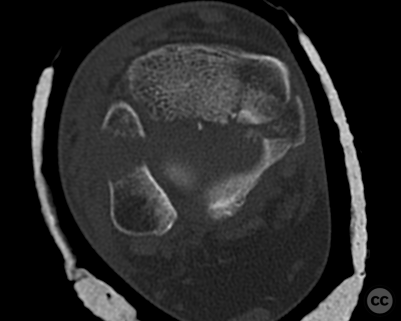
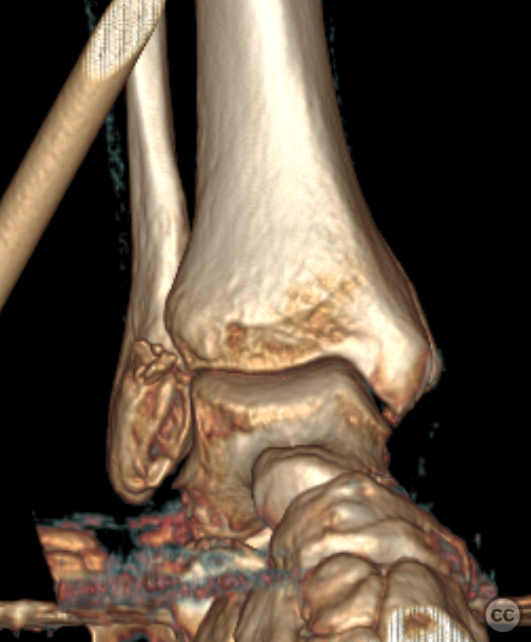
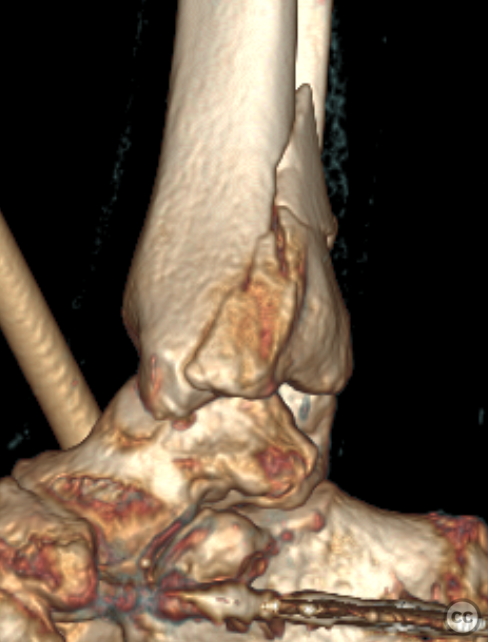
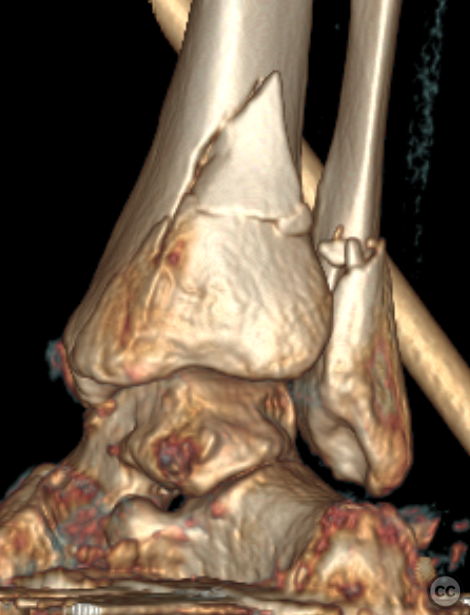
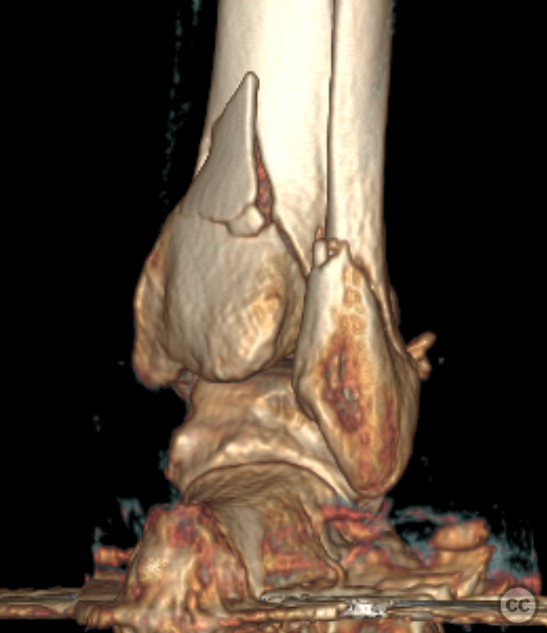
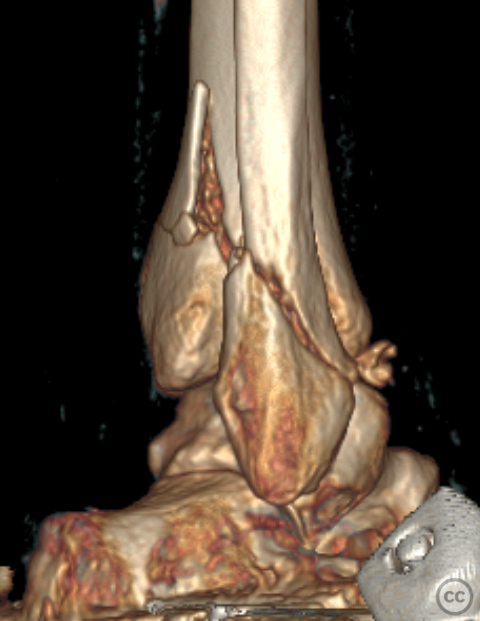
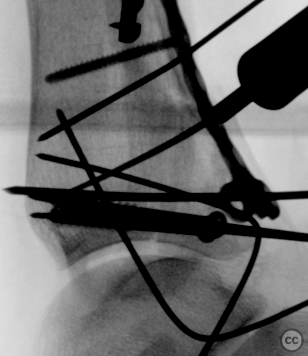
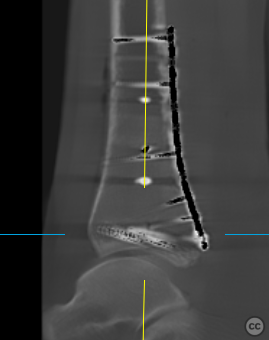
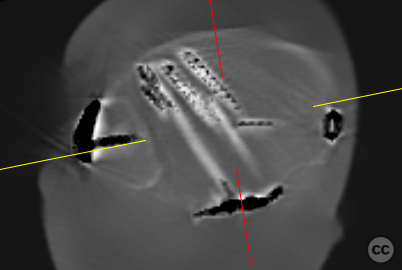
Clinical and radiological findings: A 62-year-old osteoporotic female sustained a right ankle fracture following a domestic trip and fall. Initial clinical examination revealed a subluxed joint post-reduction, confirmed by plain film and CT imaging. The fracture pattern included a large Mason and Molly Type 3 posterior malleolus fracture, a transsyndesmotic fibula fracture, and a partial rupture of the deltoid ligament medially. Temporizing external fixation was applied prior to definitive management.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The planned surgical approach involved a posteromedial incision for the posterior malleolus fracture and a lateral approach for the fibula fracture.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on the operating table with a tourniquet applied to the right thigh. A wedge was placed under the ipsilateral pelvis to facilitate internal and external rotation of the lower limb intraoperatively. The figure-four positio
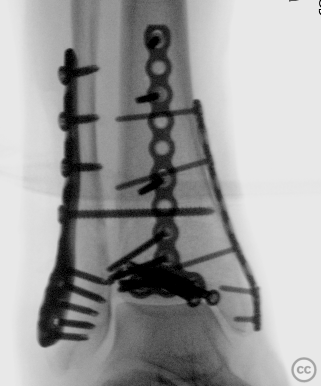
Anatomical surgical approach: A curved medial incision over the posterior aspect of the medial malleolus was performed, followed by subcutaneous dissection. The vena saphena magna was identified and preserved. The musculi tibialis posterior and flexor hallucis longus were identified, with working windows established lateral to the musculus flexor hallucis longus and medial to the musculus tibialis posterior. Open reduction of the posterior malleolus fracture was achieved, followed by initial Kirschner wire fixation and placement of two 4.0-millimeter cannulated screws. A posterolaterally positioned buttress plate (2.7 millimeters) from the Stryker Mini Frag set was applied. A posteromedial plate (2.4 millimeters) from the Stryker Mini Fragment set was then applied to the medial malleolus.A longitudinal incision overlying the fibula was made, followed by subcutaneous dissection and identification of the nervus peroneus superficialis, which was mobilized anteriorly and protected. Subperiosteal elevation revealed an anterior tibial-sided avulsion at syndesmosis fibers. Reduction and temporary fixation with Kirschner wires were performed before placing a 3.5/2.7-millimeter lateral locking plate from Synthes.
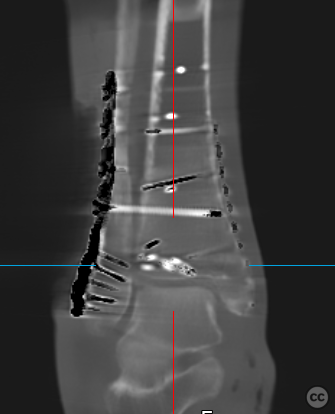
Operative remarks:Multiplanar fluoroscopy confirmed restoration of ankle mortise geometry. The tibial-sided avulsion at syndesmosis was fixed using a TwinFix suture anchor placed in its footprint, reattaching both syndesmotic fibers and bony fragments to their origin points. A tricortical syndesmosis screw was placed under fluoroscopic guidance before performing an intraoperative 3D Cone Beam CT scan that confirmed anatomic joint reduction without intra-articular screw misplacement.
Postoperative protocol: Not specified
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: - 4.0-millimeter cannulated screws - 2.7-millimeter Stryker Mini Frag buttress plate - 2.4-millimeter Stryker Mini Fragment plate - 3.5/2.7-millimeter Synthes lateral locking plate - TwinFix suture anchor - Tricortical syndesmosis screw
Search for Related Literature
Dr Ed Oates
- Germany , Schleswig Holstein
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
Article viewed 566 times
17 Jul 2024
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Oates, E.J. (2024). Mason and Molly Type 3 Posterior Malleolus Fracture with Transsyndesmotic Fibula Fracture. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 44671874 Published Online Jul 17 2024.