Exploration and Neurolysis for Persistent Neuropathic Pain Post-Weber B Fracture Fixation
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
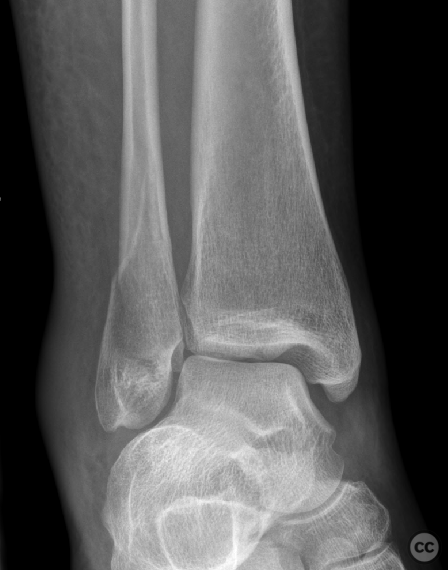
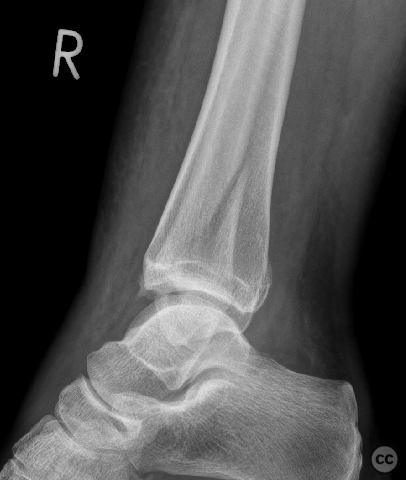
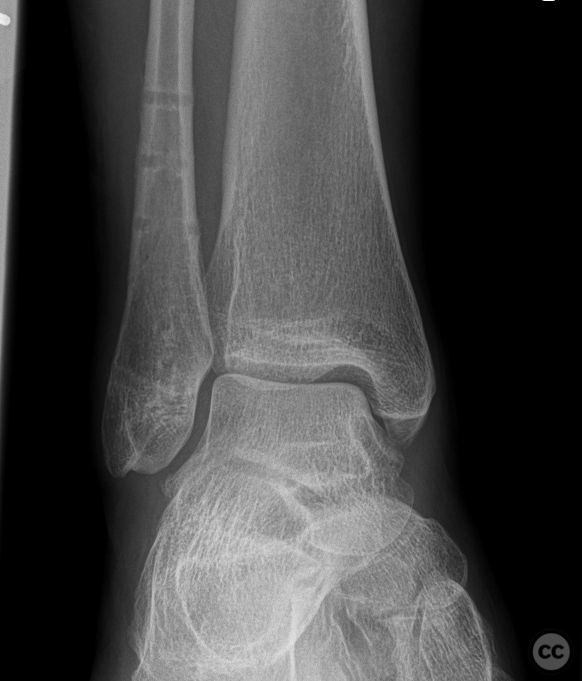
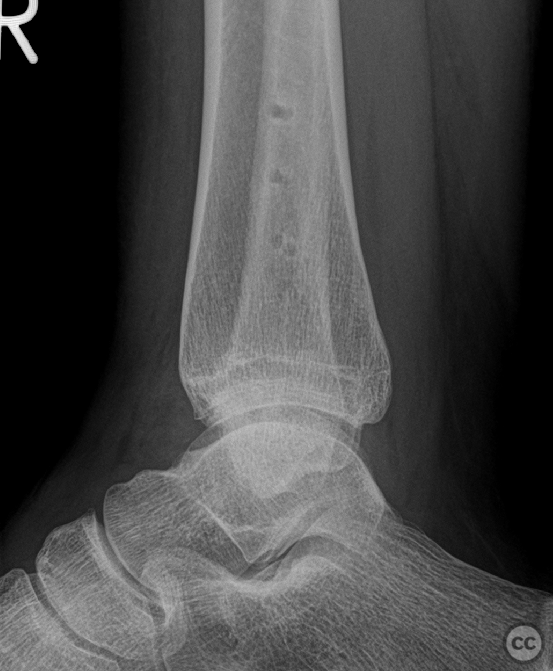
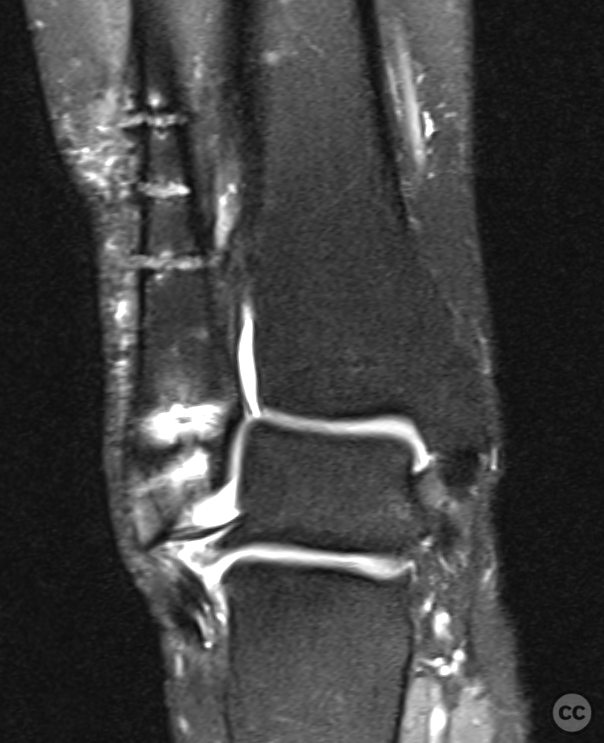
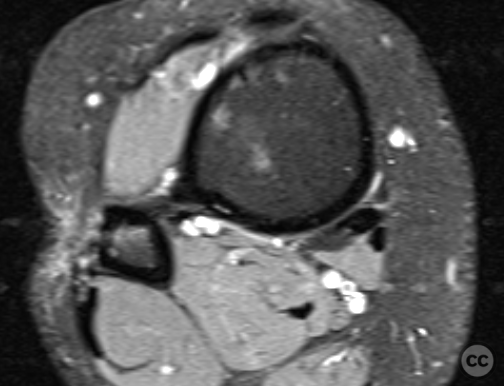
Clinical and radiological findings: Patient presented with a history of Weber B fracture of the right distal fibula, treated surgically with subsequent removal of hardware. Post index OP, the patient had developed hypersensitivity and sensory disturbances along the lateral aspect of the foot, worsening since hardware removal. MRI investigations did not reveal any neuroma. Despite physiotherapy, which slightly improved symptoms, the neuropathic pain persisted, particularly along the lateral lower leg radiating to the 4th and 5th toes. The proximal scar area was notably tender, with pain radiating distally. Medications such as Pregabalin and Gabapentin were not tolerated by the patient.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: Given the lack of improvement with conservative management, surgical exploration and neurolysis of the superficial peroneal nerve were planned.
Surgical Discussion
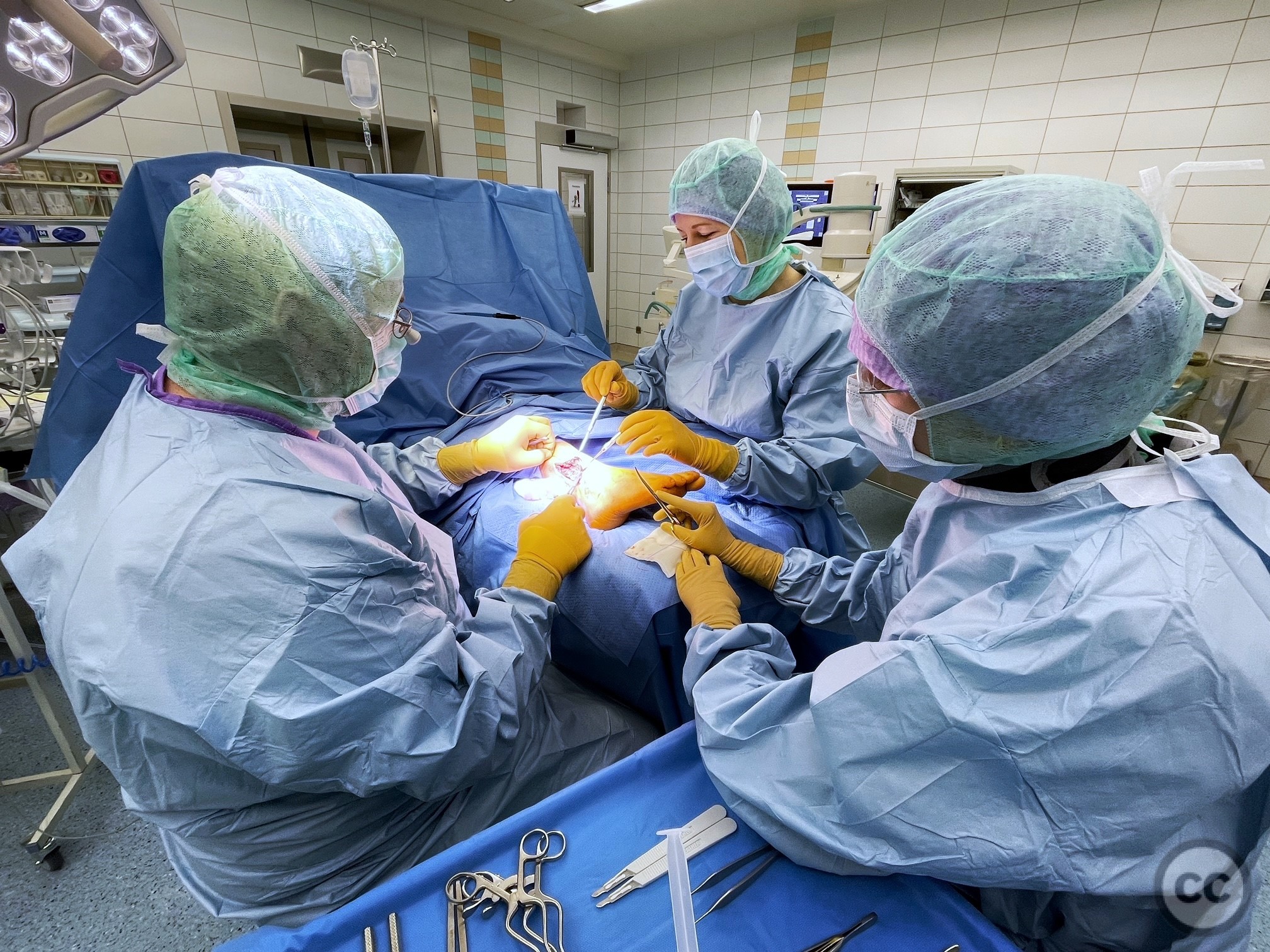
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine with a bump under the hip to internally rotate the lower limb, facilitating access to the lateral aspect of the leg.
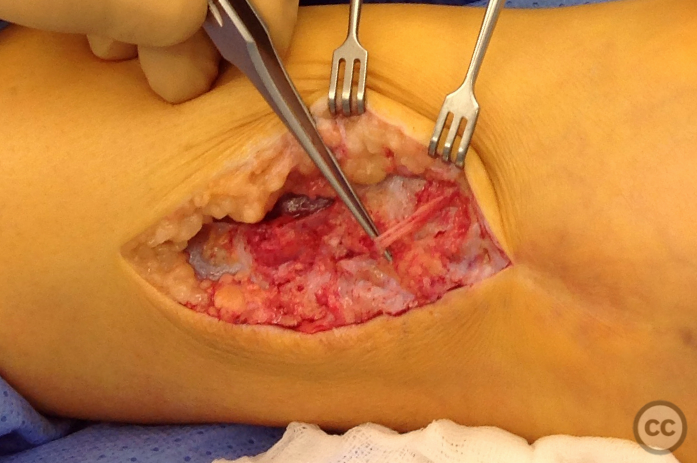
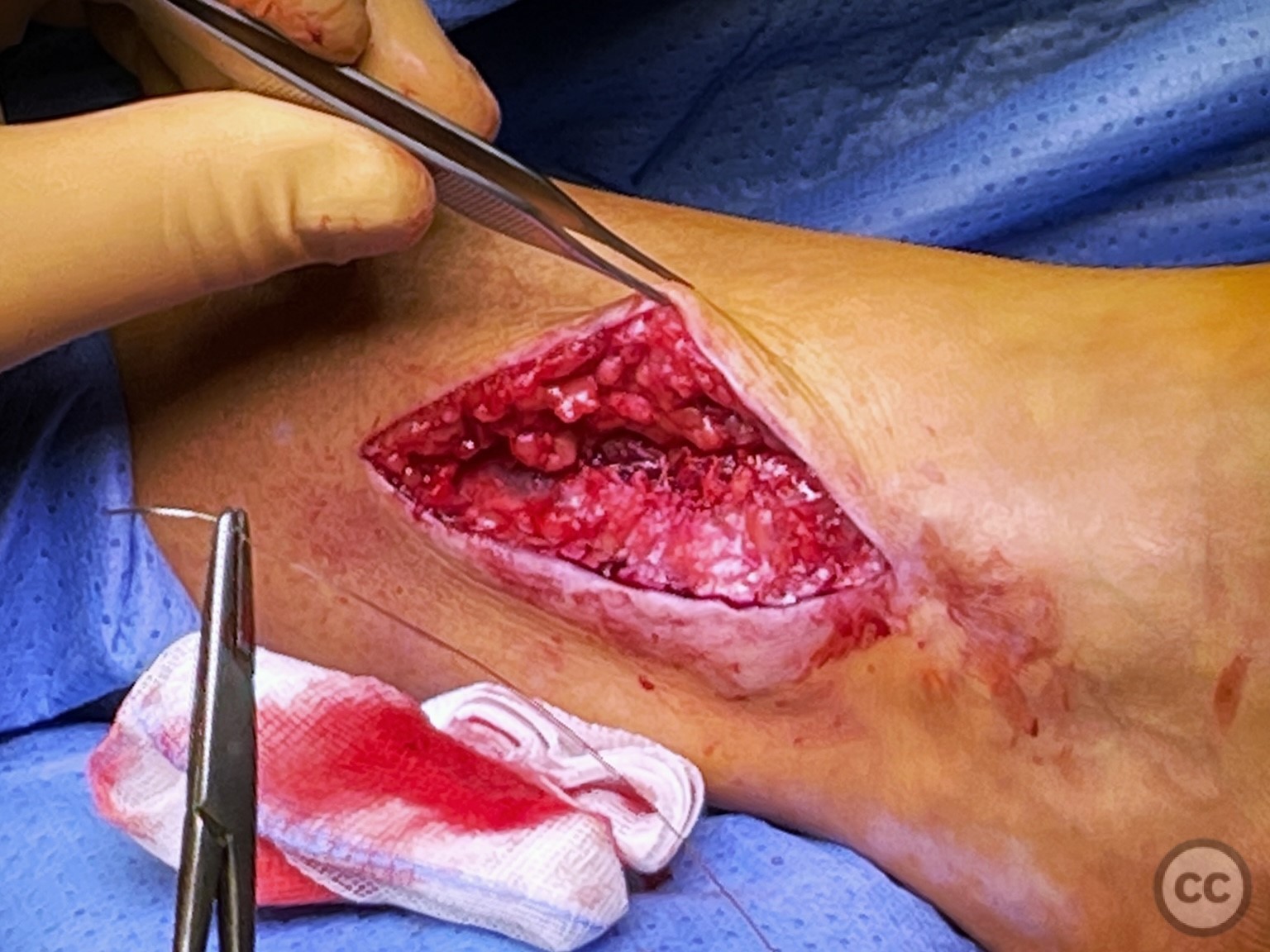
Anatomical surgical approach: A longitudinal incision was made along the lateral aspect of the leg over the previous surgical site. Initial superficial dissection did not reveal the superficial peroneal nerve. Further exploration in the region of the original plate bed identified the nerve adherent to the bone with marked adhesions and reduced caliber, suggesting taht the nerve had been trapped under the plate at the time of original fixation.
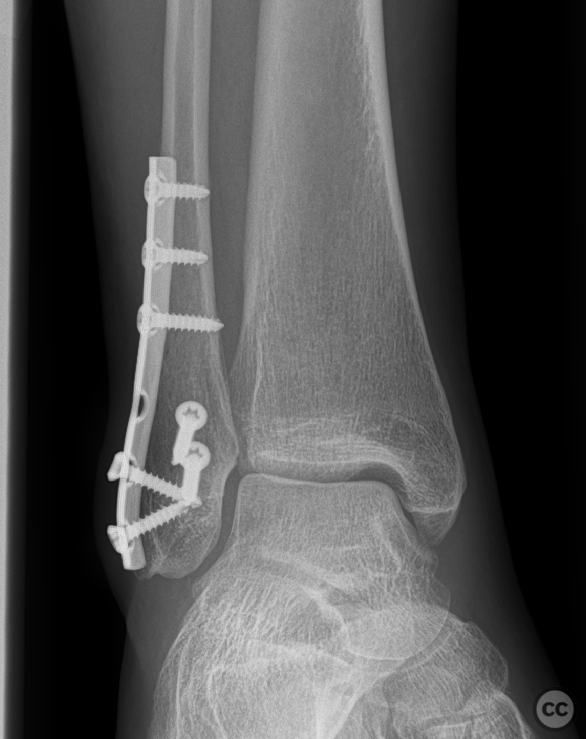
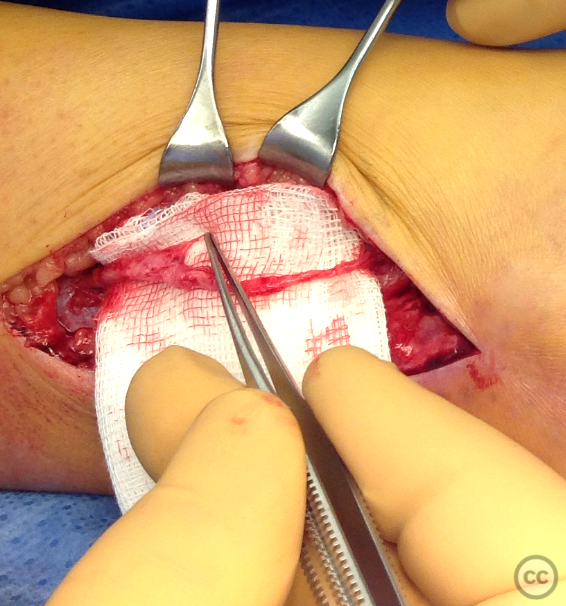
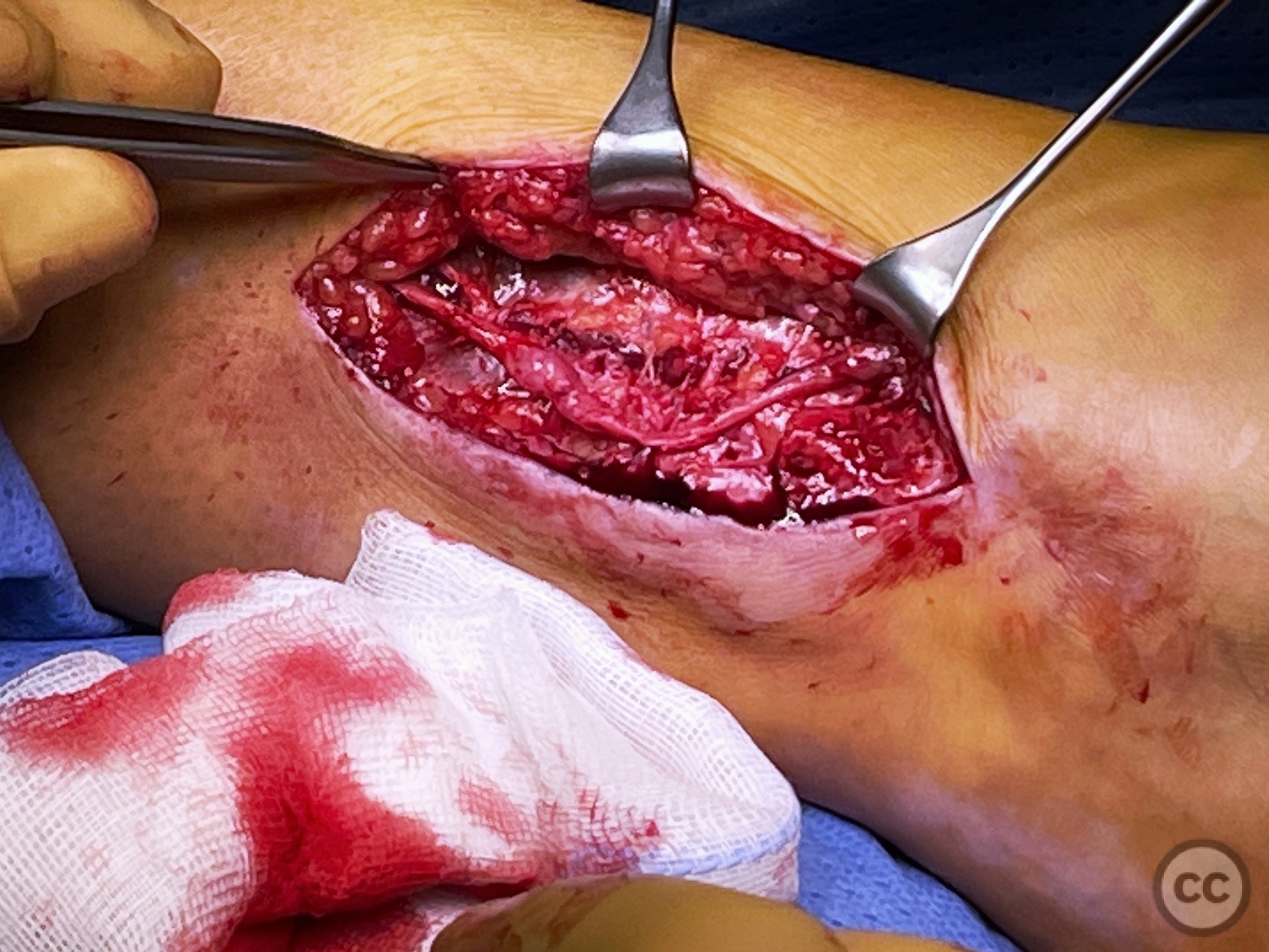
Operative remarks:Neurolysis was performed proximally and distally around the adherent section of the nerve, which was swollen and inflamed immediately proximal to its fibular traversal. The nerve was mobilized over approximately 10cm and transposed to a soft tissue bed anterior to the fibula to help prevent irritation over the bony fibular margin. Closure was achieved in layers.
Postoperative protocol: Not specified
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: No implants used in this procedure.
Author's Resources & References
Search for Related Literature
Dr Ed Oates
- Germany , Schleswig Holstein
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities

Article viewed 428 times
15 Mar 2024
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Oates, E.J. (2024). Exploration and Neurolysis for Persistent Neuropathic Pain Post-Weber B Fracture Fixation. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 46236263 Published Online Mar 15 2024.