Displaced Greater Tuberosity Fracture
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
Clinical and radiological findings: A 34-year-old male sustained a work-related injury resulting in a displaced fracture of the greater tuberosity of the humerus. The patient did not present with any associated neurovascular injury.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The planned surgical approach involved a transdeltoid incision to access the fracture site. The reduction was to be achieved by passing sutures through the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons, followed by temporary fixation with a Kirschner wire and definitive fixation with a cancellous screw and transosseous sutures.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned in a beach chair position to facilitate optimal access to the shoulder joint.
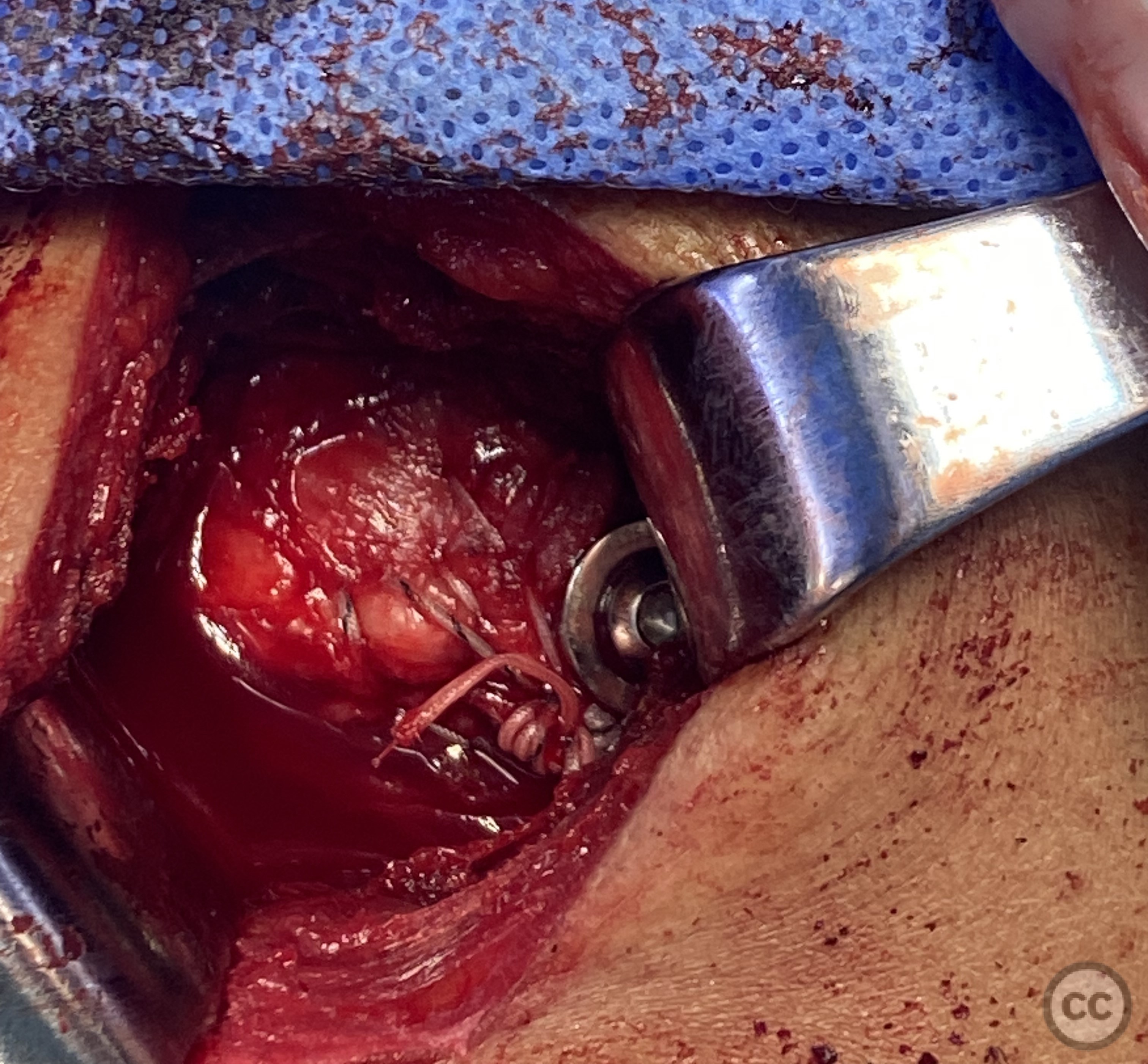
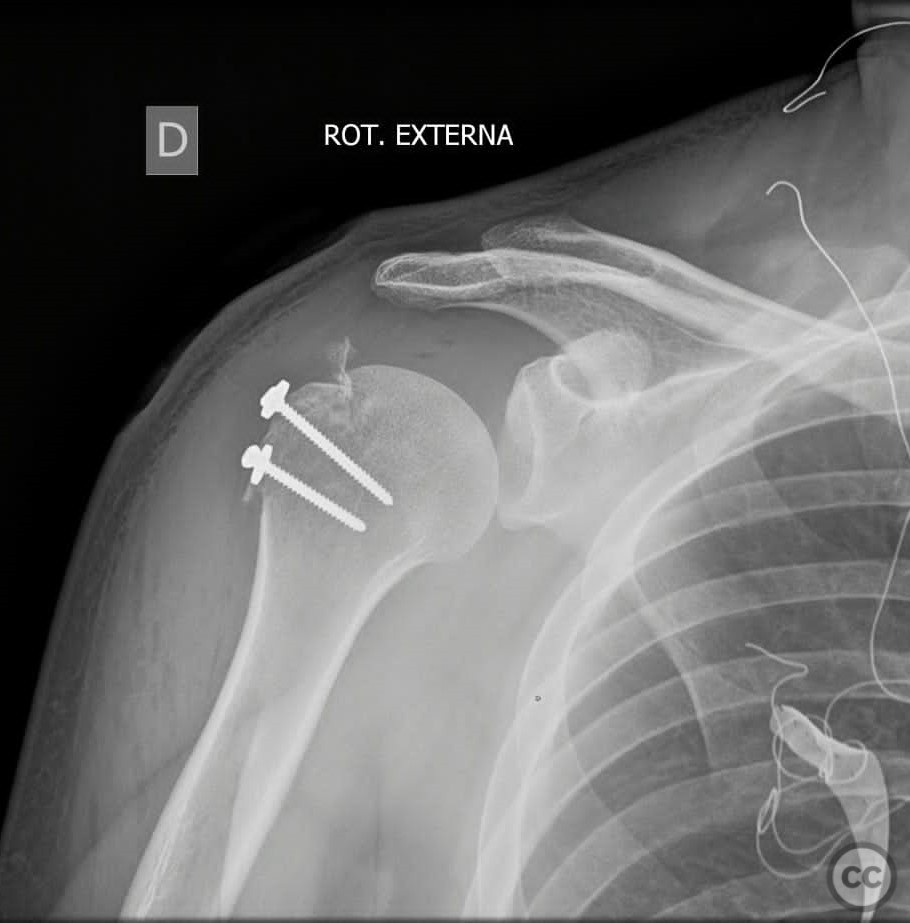
Anatomical surgical approach: A transdeltoid approach was utilized, involving an incision through the deltoid muscle to expose the greater tuberosity. Sutures were passed through the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons to aid in the reduction of the fracture. The fragment was temporarily fixed with a Kirschner wire, and reduction was verified. Definitive fixation was achieved using a cancellous screw and transosseous sutures.
Operative remarks:The reduction of the greater tuberosity fragment was confirmed intraoperatively. The use of both a Kirschner wire for temporary stabilization and a cancellous screw for definitive fixation ensured adequate stability of the fracture. Transosseous sutures provided additional support to maintain the reduction.
Postoperative protocol: Postoperative rehabilitation included immobilization of the shoulder in a sling for 4 weeks, followed by passive range of motion exercises. Active range of motion exercises were initiated at 6 weeks postoperatively, with gradual progression to strengthening exercises by 12 weeks.
Follow up: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: - Kirschner wire - Cancellous screw - Transosseous sutures
Search for Related Literature
Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities
 10.28.23 a. m..jpeg)


Article viewed 498 times
22 Jul 2024
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
LUIS LEONCIO TEMOCHE DIAZ. (2024). Displaced Greater Tuberosity Fracture. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 6152086 Published Online Jul 22 2024.