Salter-Harris II Distal Tibia Fracture
Score and Comment on this Case
Clinical Details
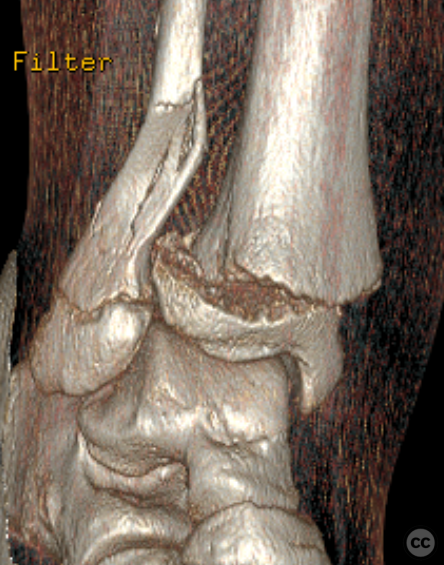
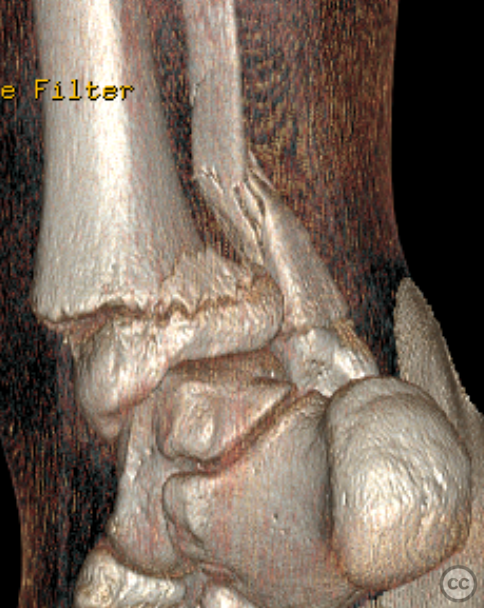
Clinical and radiological findings: A 13-year-old male presented following a fall from an e-scooter. The patient, who is large framed and overweight for his age, sustained a closed right ankle injury. Initial plain film imaging demonstrated a classic Salter-Harris type II distal tibia fracture with an associated suprasyndesmotic fibula fracture. A subsequent CT scan confirmed the absence of any triplanar epiphyseal component.
Preoperative Plan
Planning remarks: The preoperative plan involved a closed reduction of the Salter-Harris type II fracture, followed by percutaneous fixation using Kirschner wires (K-wires). The fibula fracture was expected to reduce spontaneously with the reduction of the tibia, thus avoiding the need for additional manipulation or fixation.
Surgical Discussion
Patient positioning: The patient was positioned supine on a radiolucent operating table, with the right leg positioned at the table's edge to facilitate access and imaging.
Anatomical surgical approach: Following sterile preparation and draping, a timeout was observed, and two grams of Cefazolin antibiotics were administered. A closed reduction of the Salter-Harris type II distal tibia fracture was performed, achieving anatomic reduction confirmed by a satisfying click and multiplanar fluoroscopy. The fibula fracture reduced spontaneously with the tibial reduction. Percutaneous introduction of a retrograde 2 mm K-wire over the medial malleolus was performed, crossing the growth plate and engaging the lateral proximal tibial cortex. This was followed by the insertion of two additional K-wires: one anterior-to-posterior retrograde and one posterior-to-anterior medial retrograde, both engaging the contralateral cortices to provide multiaxial stability.
Operative remarks:The reduction was easily achieved and maintained throughout the procedure. Multiplanar fluoroscopy confirmed the satisfactory position of all K-wires and the maintenance of anatomic reduction. Irrigation of the entry points was followed by disinfection and application of dressings. An elastic bandage was applied to the lower limb, followed by a below-knee fiberglass cast with the foot in plantargrade flexion. Final fluoroscopy images confirmed both reduction and hardware placement.
Postoperative protocol: Not specified
Orthopaedic implants used: 2 mm Kirschner wires (K-wires)
Search for Related Literature
Dr Ed Oates
- Germany , Schleswig Holstein
- Area of Specialty - General Trauma
- Position - Specialist Consultant

Industry Sponsership
contact us for advertising opportunities








Article viewed 299 times
03 Jul 2024
Add to Bookmarks
Full Citation
Cite this article:
Oates, E.J. (2024). Salter-Harris II Distal Tibia Fracture. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. Case Report 9700198 Published Online Jul 03 2024.